Targeting of albumin-embedded paclitaxel nanoparticles to tumors
- PMID: 18829396
- PMCID: PMC2824435
- DOI: 10.1016/j.nano.2008.07.007
Targeting of albumin-embedded paclitaxel nanoparticles to tumors
Abstract
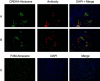
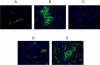
We have used tumor-homing peptides to target abraxane, a clinically approved paclitaxel-albumin nanoparticle, to tumors in mice. The targeting was accomplished with two peptides, CREKA and LyP-1 (CGNKRTRGC). Fluorescein (FAM)-labeled CREKA-abraxane, when injected intravenously into mice bearing MDA-MB-435 human cancer xenografts, accumulated in tumor blood vessels, forming aggregates that contained red blood cells and fibrin. FAM-LyP-1-abraxane co-localized with extravascular islands expressing its receptor, p32. Self-assembled mixed micelles carrying the homing peptide and the label on different subunits accumulated in the same areas of tumors as LyP-1-abraxane, showing that Lyp-1 can deliver intact nanoparticles into extravascular sites. Untargeted, FAM-abraxane was detected in the form of a faint meshwork in tumor interstitium. LyP-1-abraxane produced a statistically highly significant inhibition of tumor growth compared with untargeted abraxane. These results show that nanoparticles can be effectively targeted into extravascular tumor tissue and that targeting can enhance the activity of a therapeutic nanoparticle.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Preclinical efficacy studies of a novel nanoparticle-based formulation of paclitaxel that out-performs Abraxane.Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2010 Apr;65(5):923-30. doi: 10.1007/s00280-009-1099-1. Epub 2009 Aug 15. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2010. PMID: 19685054 Free PMC article.
-
An imagable and photothermal "Abraxane-like" nanodrug for combination cancer therapy to treat subcutaneous and metastatic breast tumors.Adv Mater. 2015 Feb 4;27(5):903-10. doi: 10.1002/adma.201404308. Epub 2014 Dec 12. Adv Mater. 2015. PMID: 25504416
-
18F-FPPRGD2 and 18F-FDG PET of response to Abraxane therapy.J Nucl Med. 2011 Jan;52(1):140-6. doi: 10.2967/jnumed.110.080606. Epub 2010 Dec 13. J Nucl Med. 2011. PMID: 21149494
-
Efficient delivery of therapeutic agents by using targeted albumin nanoparticles.Adv Protein Chem Struct Biol. 2015;98:121-43. doi: 10.1016/bs.apcsb.2014.11.002. Epub 2015 Mar 3. Adv Protein Chem Struct Biol. 2015. PMID: 25819278 Review.
-
Albumin-bound paclitaxel: a next-generation taxane.Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2006 Jun;7(8):1041-53. doi: 10.1517/14656566.7.8.1041. Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2006. PMID: 16722814 Review.
Cited by
-
pH-Responsive Self-Assembling Peptide-Based Biomaterials: Designs and Applications.ACS Appl Bio Mater. 2022 May 3:10.1021/acsabm.2c00188. doi: 10.1021/acsabm.2c00188. Online ahead of print. ACS Appl Bio Mater. 2022. PMID: 35505454 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Tumor-penetrating peptides.Front Oncol. 2013 Aug 27;3:216. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2013.00216. eCollection 2013. Front Oncol. 2013. PMID: 23986882 Free PMC article.
-
Nanoparticle-induced vascular blockade in human prostate cancer.Blood. 2010 Oct 14;116(15):2847-56. doi: 10.1182/blood-2010-03-274258. Epub 2010 Jun 29. Blood. 2010. PMID: 20587786 Free PMC article.
-
Drug-induced amplification of nanoparticle targeting to tumors.Nano Today. 2014 Oct;9(5):550-559. doi: 10.1016/j.nantod.2014.09.001. Epub 2014 Sep 23. Nano Today. 2014. PMID: 29731806 Free PMC article.
-
iRGD peptide conjugation potentiates intraperitoneal tumor delivery of paclitaxel with polymersomes.Biomaterials. 2016 Oct;104:247-57. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2016.07.023. Epub 2016 Jul 20. Biomaterials. 2016. PMID: 27472162 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Jain RK. Vascular and interstitial barriers to delivery of therapeutic agents in tumors. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 1990;9:253–266. - PubMed
-
- Ferrara N, Alitalo K. Clinical applications of angiogenic growth factors and their inhibitors. Nat Med. 1999;5:1359–1364. - PubMed
-
- Hanahan D, Weinberg RA. The hallmarks of cancer. Cell. 2000;100:57–70. - PubMed
-
- Ruoslahti E. Specialization of tumor vasculature. Nat Rev Cancer. 2002;2:83–90. - PubMed
-
- Arap W, Pasqualini R, Ruoslahti E. Cancer treatment by targeted drug delivery to tumor vasculature in a mouse model. Science. 1998;279:377–380. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

