IRBIT, inositol 1,4,5-triphosphate (IP3) receptor-binding protein released with IP3, binds Na+/H+ exchanger NHE3 and activates NHE3 activity in response to calcium
- PMID: 18829453
- PMCID: PMC2586249
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M805534200
IRBIT, inositol 1,4,5-triphosphate (IP3) receptor-binding protein released with IP3, binds Na+/H+ exchanger NHE3 and activates NHE3 activity in response to calcium
Abstract
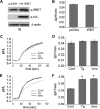
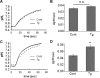
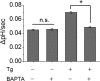
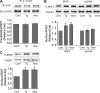
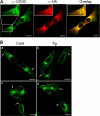
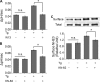
Calcium (Ca2+) is a highly versatile second messenger that regulates various cellular processes. Previous studies showed that elevation of intracellular Ca2+ regulates the activity of Na+/H+ exchanger 3 (NHE3). However, the effect of Ca2+-dependent signaling on NHE3 activity varies depending on cell types. In this study, we report the identification of IP3 receptor-binding protein released with IP3 (IRBIT) as a NHE3 interacting protein and its role in regulation of NHE3 activity. IRBIT bound to the carboxyl-terminal domain of NHE3, which is necessary for acute regulation of NHE3. Ectopic expression of IRBIT resulted in Ca2+-dependent activation of NHE3 activity, whereas silencing of endogenous IRBIT resulted in inhibition of NHE3 activity. Ca2+-dependent stimulation of NHE3 activity was dependent on the binding of IRBIT to NHE3. Previously Ca2+-dependent inhibition of NHE3 was demonstrated in the presence of NHERF2. Co-expression of IRBIT was able to reverse the NHERF2-dependent inhibition of NHE3. We also showed that IRBIT-dependent activation of NHE3 involves exocytic trafficking of NHE3 to the plasma membrane and this activation was blocked by inhibition of calmodulin (CaM) or CaM-dependent kinase II. These results suggest that the overall effect of Ca2+ on NHE3 activity is balanced by IRBIT-dependent activation and NHERF2-dependent inhibition.
Figures
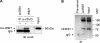


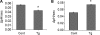

Similar articles
-
Activation of Na+/H+ exchanger NHE3 by angiotensin II is mediated by inositol 1,4,5-triphosphate (IP3) receptor-binding protein released with IP3 (IRBIT) and Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II.J Biol Chem. 2010 Sep 3;285(36):27869-78. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.133066. Epub 2010 Jun 28. J Biol Chem. 2010. PMID: 20584908 Free PMC article.
-
The NHERF1 PDZ1 domain and IRBIT interact and mediate the activation of Na+/H+ exchanger 3 by ANG II.Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2016 Aug 1;311(2):F343-51. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00247.2016. Epub 2016 Jun 8. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2016. PMID: 27279487 Free PMC article.
-
Calmodulin kinase II constitutively binds, phosphorylates, and inhibits brush border Na+/H+ exchanger 3 (NHE3) by a NHERF2 protein-dependent process.J Biol Chem. 2012 Apr 13;287(16):13442-56. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.307256. Epub 2012 Feb 27. J Biol Chem. 2012. PMID: 22371496 Free PMC article.
-
IRBIT: a regulator of ion channels and ion transporters.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014 Oct;1843(10):2195-204. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2014.01.031. Epub 2014 Feb 8. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014. PMID: 24518248 Review.
-
The role of Ca2+ signaling in cell function with special reference to exocrine secretion.Cornea. 2008 Sep;27 Suppl 1:S3-8. doi: 10.1097/ICO.0b013e31817f246e. Cornea. 2008. PMID: 18813072 Review.
Cited by
-
Distinct mechanisms underlie adaptation of proximal tubule Na+/H+ exchanger isoform 3 in response to chronic metabolic and respiratory acidosis.Pflugers Arch. 2012 Apr;463(5):703-14. doi: 10.1007/s00424-012-1092-0. Epub 2012 Mar 15. Pflugers Arch. 2012. PMID: 22419175
-
Hyperglycemia promotes microvillus membrane expression of DMT1 in intestinal epithelial cells in a PKCα-dependent manner.FASEB J. 2019 Mar;33(3):3549-3561. doi: 10.1096/fj.201801855R. Epub 2018 Nov 13. FASEB J. 2019. PMID: 30423260 Free PMC article.
-
Restoration of Na+/H+ exchanger NHE3-containing macrocomplexes ameliorates diabetes-associated fluid loss.J Clin Invest. 2015 Sep;125(9):3519-31. doi: 10.1172/JCI79552. Epub 2015 Aug 10. J Clin Invest. 2015. PMID: 26258413 Free PMC article.
-
Activation of Na+/H+ exchanger NHE3 by angiotensin II is mediated by inositol 1,4,5-triphosphate (IP3) receptor-binding protein released with IP3 (IRBIT) and Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II.J Biol Chem. 2010 Sep 3;285(36):27869-78. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.133066. Epub 2010 Jun 28. J Biol Chem. 2010. PMID: 20584908 Free PMC article.
-
A Novel Peptide Prevents Enterotoxin- and Inflammation-Induced Intestinal Fluid Secretion by Stimulating Sodium-Hydrogen Exchanger 3 Activity.Gastroenterology. 2023 Oct;165(4):986-998.e11. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2023.06.028. Epub 2023 Jul 8. Gastroenterology. 2023. PMID: 37429363 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Berridge, M. J., Bootman, M. D., and Roderick, H. L. (2003) Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell. Biol. 4 517-529 - PubMed
-
- Berridge, M. J., Lipp, P., and Bootman, M. D. (2000) Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1 11-21 - PubMed
-
- Mikoshiba, K. (2007) J. Neurochem. 102 1426-1446 - PubMed
-
- Ando, H., Mizutani, A., Matsu-ura, T., and Mikoshiba, K. (2003) J. Biol. Chem. 278 10602-10612 - PubMed
-
- Ando, H., Mizutani, A., Kiefer, H., Tsuzurugi, D., Michikawa, T., and Mikoshiba, K. (2006) Mol. Cell 22 795-806 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

