Potent and selective disruption of protein kinase D functionality by a benzoxoloazepinolone
- PMID: 18829454
- PMCID: PMC2586241
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M805358200
Potent and selective disruption of protein kinase D functionality by a benzoxoloazepinolone
Abstract
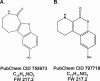
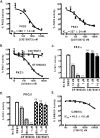
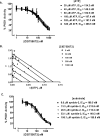
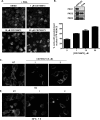
Protein kinase D (PKD) is a novel family of serine/threonine kinases targeted by the second messenger diacylglycerol. It has been implicated in many important cellular processes and pathological conditions. However, further analysis of PKD in these processes is severely hampered by the lack of a PKD-specific inhibitor that can be readily applied to cells and in animal models. We now report the discovery of the first potent and selective cell-active small molecule inhibitor for PKD, benzoxoloazepinolone (CID755673). This inhibitor was identified from the National Institutes of Health small molecule repository library of 196,173 compounds using a human PKD1 (PKCmu)-based fluorescence polarization high throughput screening assay. CID755673 suppressed half of the PKD1 enzyme activity at 182 nm and exhibited selective PKD1 inhibition when compared with AKT, polo-like kinase 1 (PLK1), CDK activating kinase (CAK), CAMKIIalpha, and three different PKC isoforms. Moreover, it was not competitive with ATP for enzyme inhibition. In cell-based assays, CID755673 blocked phorbol ester-induced endogenous PKD1 activation in LNCaP cells in a concentration-dependent manner. Functionally, CID755673 inhibited the known biological actions of PKD1 including phorbol ester-induced class IIa histone deacetylase 5 nuclear exclusion, vesicular stomatitis virus glycoprotein transport from the Golgi to the plasma membrane, and the ilimaquinone-induced Golgi fragmentation. Moreover, CID755673 inhibited prostate cancer cell proliferation, cell migration, and invasion. In summary, our findings indicate that CID755673 is a potent and selective PKD1 inhibitor with valuable pharmacological and cell biological potential.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Discovery of diverse small molecule chemotypes with cell-based PKD1 inhibitory activity.PLoS One. 2011;6(10):e25134. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0025134. Epub 2011 Oct 5. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 21998636 Free PMC article.
-
TAK-960, a novel, orally available, selective inhibitor of polo-like kinase 1, shows broad-spectrum preclinical antitumor activity in multiple dosing regimens.Mol Cancer Ther. 2012 Mar;11(3):700-9. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-11-0762. Epub 2011 Dec 21. Mol Cancer Ther. 2012. PMID: 22188812
-
CID755673 enhances mitogenic signaling by phorbol esters, bombesin and EGF through a protein kinase D-independent pathway.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2010 Jan 1;391(1):63-8. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2009.11.002. Epub 2009 Nov 5. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2010. PMID: 19896460 Free PMC article.
-
Developments of polo-like kinase 1 (Plk1) inhibitors as anti-cancer agents.Mini Rev Med Chem. 2013 Dec;13(14):2014-25. doi: 10.2174/13895575113136660103. Mini Rev Med Chem. 2013. PMID: 24160708 Review.
-
Polo-like kinases inhibitors.Curr Med Chem. 2012;19(23):3937-48. doi: 10.2174/092986712802002455. Curr Med Chem. 2012. PMID: 22709006 Review.
Cited by
-
A protein kinase C/protein kinase D pathway protects LNCaP prostate cancer cells from phorbol ester-induced apoptosis by promoting ERK1/2 and NF-{kappa}B activities.Carcinogenesis. 2011 Aug;32(8):1198-206. doi: 10.1093/carcin/bgr113. Epub 2011 Jun 10. Carcinogenesis. 2011. PMID: 21665893 Free PMC article.
-
Inducible Inhibition of Gβγ Reveals Localization-dependent Functions at the Plasma Membrane and Golgi.J Biol Chem. 2017 Feb 3;292(5):1773-1784. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M116.750430. Epub 2016 Dec 19. J Biol Chem. 2017. PMID: 27994056 Free PMC article.
-
Ras/Raf/MEK/ERK and PI3K/PTEN/Akt/mTOR cascade inhibitors: how mutations can result in therapy resistance and how to overcome resistance.Oncotarget. 2012 Oct;3(10):1068-111. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.659. Oncotarget. 2012. PMID: 23085539 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Protein kinase d regulates cell death pathways in experimental pancreatitis.Front Physiol. 2012 Mar 27;3:60. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2012.00060. eCollection 2012. Front Physiol. 2012. PMID: 22470346 Free PMC article.
-
Small Molecule Inhibitors of Protein Kinase D: Early Development, Current Approaches, and Future Directions.J Med Chem. 2023 Jan 12;66(1):122-139. doi: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.2c01599. Epub 2022 Dec 20. J Med Chem. 2023. PMID: 36538005 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Manning, G., Whyte, D. B., Martinez, R., Hunter, T., and Sudarsanam, S. (2002) Science 298 1912-1934 - PubMed
-
- Wang, Q. J. (2006) Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 27 317-323 - PubMed
-
- Hayashi, A., Seki, N., Hattori, A., Kozuma, S., and Saito, T. (1999) Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1450 99-106 - PubMed
-
- Johannes, F. J., Prestle, J., Eis, S., Oberhagemann, P., and Pfizenmaier, K. (1994) J. Biol. Chem. 269 6140-6148 - PubMed
-
- Sturany, S., Van Lint, J., Muller, F., Wilda, M., Hameister, H., Hocker, M., Brey, A., Gern, U., Vandenheede, J., Gress, T., Adler, G., and Seufferlein, T. (2001) J. Biol. Chem. 276 3310-3318 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Chemical Information
Miscellaneous

