Therapeutic IMC-C225 antibody inhibits breast cancer cell invasiveness via Vav2-dependent activation of RhoA GTPase
- PMID: 18829495
- PMCID: PMC3151536
- DOI: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-07-5288
Therapeutic IMC-C225 antibody inhibits breast cancer cell invasiveness via Vav2-dependent activation of RhoA GTPase
Abstract
Purpose: Abnormalities in the expression and signaling pathways downstream of epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) contribute to progression, invasion, and maintenance of the malignant phenotype in human cancers. Accordingly, biological agents, such as the EGFR-blocking antibody IMC-C225 have promising anticancer potential and are currently in various stages of clinical development. Because use of IMC-C225 is limited, at present, only for treatment of cancer with high EGFR expression, the goal of the present study was to determine the effect of IMC-C225 on the invasiveness of breast cancer cells with high and low levels of EGFR expression.
Experimental design: The effect of IMC-C225 on invasion was studied using breast cancer cell lines with high and low levels of EGFR expression.
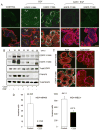
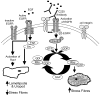
Results: The addition of EGF led to progressive stress fiber dissolution. In contrast, cells treated with IMC-C225 showed reduced invasiveness and increased stress-fiber formation. Interestingly, IMC-C225 pretreatment was accompanied by EGFR phosphorylation, as detected using an anti-phosphorylated tyrosine antibody (PY99), which correlated with phosphorylation of Vav2 guanine nucleotide exchange factor and activation of RhoA GTPase irrespective of EGFR level, and Vav2 interacted with EGFR only in IMC-C225-treated cells. The underlying mechanism involved an enhanced interaction between beta1 integrins and EGFR upon IMC-C225 treatment.
Conclusion: Here, we defined a new mechanism for IMC-C225 that cross-links integrins with EGFR, leading to activation of RhoA and inhibition of breast cancer cell invasion irrespective of the level of EGFR in the cells, thus providing a rationale for using IMC-C225 in the metastatic setting independent of the levels of EGFR.
Figures

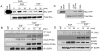


Similar articles
-
Treatment of pancreatic cancer xenografts with Erbitux (IMC-C225) anti-EGFR antibody, gemcitabine, and radiation.Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2002 Nov 15;54(4):1180-93. doi: 10.1016/s0360-3016(02)03788-4. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2002. PMID: 12419447
-
Epidermal growth factor receptors as a target for cancer treatment: the emerging role of IMC-C225 in the treatment of lung and head and neck cancers.Semin Oncol. 2002 Feb;29(1 Suppl 4):27-36. doi: 10.1053/sonc.2002.31525. Semin Oncol. 2002. PMID: 11894011 Review.
-
Antitumor activity of ZD6474, a vascular endothelial growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor, in human cancer cells with acquired resistance to antiepidermal growth factor receptor therapy.Clin Cancer Res. 2004 Jan 15;10(2):784-93. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.ccr-1100-03. Clin Cancer Res. 2004. PMID: 14760102
-
IMC-C225, an anti-epidermal growth factor receptor monoclonal antibody, for treatment of head and neck cancer.Expert Opin Biol Ther. 2001 Jul;1(4):719-32. doi: 10.1517/14712598.1.4.719. Expert Opin Biol Ther. 2001. PMID: 11727507 Review.
-
IMC-C225, an anti-epidermal growth factor receptor monoclonal antibody for treatment of head and neck cancer.Semin Oncol. 2002 Oct;29(5 Suppl 14):18-30. doi: 10.1053/sonc.2002.35644. Semin Oncol. 2002. PMID: 12422310 Review.
Cited by
-
ARF1 regulates the Rho/MLC pathway to control EGF-dependent breast cancer cell invasion.Mol Biol Cell. 2014 Jan;25(1):17-29. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E13-06-0335. Epub 2013 Nov 6. Mol Biol Cell. 2014. PMID: 24196838 Free PMC article.
-
The actin targeting compound Chondramide inhibits breast cancer metastasis via reduction of cellular contractility.PLoS One. 2014 Nov 12;9(11):e112542. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0112542. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25391145 Free PMC article.
-
Dual kinase inhibition of EGFR and HER2 overcomes resistance to cetuximab in a novel in vivo model of acquired cetuximab resistance.Clin Cancer Res. 2011 Sep 15;17(18):5935-44. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-11-0370. Epub 2011 Jul 26. Clin Cancer Res. 2011. PMID: 21791633 Free PMC article.
-
SMURF1 plays a role in EGF-induced breast cancer cell migration and invasion.Mol Cells. 2013 Dec;36(6):548-55. doi: 10.1007/s10059-013-0233-4. Epub 2013 Nov 14. Mol Cells. 2013. PMID: 24241683 Free PMC article.
-
Phosphorylation-mediated regulation of GEFs for RhoA.Cell Adh Migr. 2014;8(1):11-8. doi: 10.4161/cam.28058. Epub 2013 Jan 1. Cell Adh Migr. 2014. PMID: 24589508 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Mendelsohn J, Baselga J. The EGF receptor family as targets for cancer therapy. Oncogene. 2000;19:6550–65. - PubMed
-
- Baselga J, Pfister D, Cooper MR, et al. Phase I studies of anti-epidermal growth factor receptor chimeric antibody C225 alone and in combination with cisplatin. J Clin Oncol. 2000;18:904–14. - PubMed
-
- Li S, Schmitz KR, Jeffrey PD, Wiltzius JJ, Kussie P, Ferguson KM. Structural basis for inhibition of the epidermal growth factor receptor by cetuximab. Cancer Cell. 2005;7:301–11. - PubMed
-
- Yu X, Miyamoto S, Mekada E. Integrin alpha 2 beta 1-dependent EGF receptor activation at cell-cell contact sites. J Cell Sci. 2000;113 ( Pt 12):2139–47. - PubMed
-
- Alam N, Goel HL, Zarif MJ, et al. The integrin-growth factor receptor duet. J Cell Physiol. 2007;213:649–53. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

