Validation of the p21-activated kinases as targets for inhibition in neurofibromatosis type 2
- PMID: 18829550
- PMCID: PMC2707059
- DOI: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-08-0866
Validation of the p21-activated kinases as targets for inhibition in neurofibromatosis type 2
Abstract
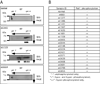
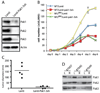
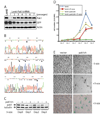
Neurofibromatosis type 2 (NF2) is a dominantly inherited cancer disorder caused by mutations at the NF2 gene locus. Merlin, the protein product of the NF2 gene, has been shown to negatively regulate Rac1 signaling by inhibiting its downstream effector kinases, the p21-activated kinases (Pak). Given the implication of Paks in tumorigenesis, it is plausible that merlin's tumor suppressive function might be mediated, at least in part, via inhibition of the Paks. We present data indicating this is indeed the case. First, analysis of primary schwannoma samples derived from NF2 patients showed that in a significant fraction of the tumors, the activity of Pak1 was highly elevated. Second, we used shRNAs to knockdown Pak1, 2, and 3 in NIH3T3 cells expressing a dominant-negative form of merlin, NF2(BBA) (NIH3T3/NF2(BBA)), and find that simultaneous knockdown of Pak1-3 in these cells significantly reduced their growth rates in vitro and inhibited their ability to form tumors in vivo. Finally, while attempting to silence Pak1 in rat schwannoma cells, we found that these cells were unable to tolerate long-term Pak1 inhibition and rapidly moved to restore Pak1 levels by shutting down Pak1 shRNA expression through a methylation-dependent mechanism. These data suggest that inhibiting Pak could be a beneficial approach for the development of therapeutics toward NF2. In addition, the finding that the shRNA-mediated Pak1 suppression was silenced rapidly by methylation raises questions about the future application of such technologies for the treatment of diseases such as cancer.
Figures

Similar articles
-
FRAX597, a small molecule inhibitor of the p21-activated kinases, inhibits tumorigenesis of neurofibromatosis type 2 (NF2)-associated Schwannomas.J Biol Chem. 2013 Oct 4;288(40):29105-14. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.510933. Epub 2013 Aug 19. J Biol Chem. 2013. PMID: 23960073 Free PMC article.
-
PAK1 inhibition reduces tumor size and extends the lifespan of mice in a genetically engineered mouse model of Neurofibromatosis Type 2 (NF2).Hum Mol Genet. 2021 Aug 12;30(17):1607-1617. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddab106. Hum Mol Genet. 2021. PMID: 34075397 Free PMC article.
-
A clue to the therapy of neurofibromatosis type 2: NF2/merlin is a PAK1 inhibitor.Cancer J. 2004 Jan-Feb;10(1):20-6. doi: 10.1097/00130404-200401000-00006. Cancer J. 2004. PMID: 15000491
-
p21-activated kinase 1: PAK'ed with potential.Oncotarget. 2011 Jun;2(6):491-6. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.271. Oncotarget. 2011. PMID: 21653999 Free PMC article. Review.
-
PAK1 as a therapeutic target.Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2010 Jul;14(7):703-25. doi: 10.1517/14728222.2010.492779. Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2010. PMID: 20507214 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
P21 activated kinases: structure, regulation, and functions.Small GTPases. 2014;5:e28003. doi: 10.4161/sgtp.28003. Epub 2014 Mar 21. Small GTPases. 2014. PMID: 24658305 Free PMC article. Review.
-
P21-activated kinase in inflammatory and cardiovascular disease.Cell Signal. 2014 Sep;26(9):2060-9. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2014.04.020. Epub 2014 May 2. Cell Signal. 2014. PMID: 24794532 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Rac1 controls Schwann cell myelination through cAMP and NF2/merlin.J Neurosci. 2012 Nov 28;32(48):17251-61. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2461-12.2012. J Neurosci. 2012. PMID: 23197717 Free PMC article.
-
Contribution of persistent C-Jun N-terminal kinase activity to the survival of human vestibular schwannoma cells by suppression of accumulation of mitochondrial superoxides.Neuro Oncol. 2011 Sep;13(9):961-73. doi: 10.1093/neuonc/nor068. Epub 2011 Jun 22. Neuro Oncol. 2011. PMID: 21697181 Free PMC article.
-
A splicing variant of Merlin promotes metastasis in hepatocellular carcinoma.Nat Commun. 2015 Oct 7;6:8457. doi: 10.1038/ncomms9457. Nat Commun. 2015. PMID: 26443326 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Yohay KH. The genetic and molecular pathogenesis of NF1 and NF2. Semin Pediatr Neurol. 2006;13:21–26. - PubMed
-
- Kissil JL, Johnson KC, Eckman MS, Jacks T. Merlin phosphorylation by p21-activated kinase 2 and effects of phosphorylation on merlin localization. J Biol Chem. 2002;277:10394–10399. - PubMed
-
- Xiao GH, Beeser A, Chernoff J, Testa JR. p21-activated kinase links Rac/Cdc42 signaling to merlin. J Biol Chem. 2002;277:883–886. - PubMed
-
- Alfthan K, Heiska L, Gronholm M, Renkema GH, Carpen O. Cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase phosphorylates merlin at serine 518 independently of p21-activated kinase and promotes merlin-ezrin heterodimerization. J Biol Chem. 2004;279:18559–18566. - PubMed
-
- Jin H, Sperka T, Herrlich P, Morrison H. Tumorigenic transformation by CPI-17 through inhibition of a merlin phosphatase. Nature. 2006;442:576–579. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

