Segmental expression of the bradykinin type 2 receptor in rat efferent ducts and epididymis and its role in the regulation of aquaporin 9
- PMID: 18829705
- PMCID: PMC2804812
- DOI: 10.1095/biolreprod.108.070797
Segmental expression of the bradykinin type 2 receptor in rat efferent ducts and epididymis and its role in the regulation of aquaporin 9
Abstract
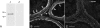
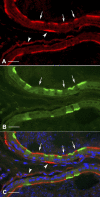
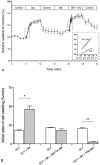
Water and solute transport in the efferent ducts and epididymis are important for the establishment of the appropriate luminal environment for sperm maturation and storage. Aquaporin 9 (AQP9) is the main water channel in the epididymis, but its regulation is still poorly understood. Components of the kinin-kallikrein system (KKS), leading to the production of bradykinin (BK), are highly expressed in the lumen of the male reproductive tract. We report here that the epididymal luminal fluid contains a significant amount of BK (2 nM). RT-PCR performed on epididymal epithelial cells isolated by laser capture microdissection (LCM) showed abundant BK type 2 receptor (Bdkrb2) mRNA expression but no type 1 receptor (Bdkrb1). Double-immunofluorescence staining for BDKRB2 and the anion exchanger AE2 (a marker of efferent duct ciliated cells) or the V-ATPase E subunit, official symbol ATP6V1E1 (a marker of epididymal clear cells), showed that BDKRB2 is expressed in the apical pole of nonciliated cells (efferent ducts) and principal cells (epididymis). Triple labeling for BDKRB2, AQP9, and ATP6V1E1 showed that BDKRB2 and AQP9 colocalize in the apical stereocilia of principal cells in the cauda epididymidis. While uniform Bdkrb2 mRNA expression was detected in the efferent ducts and along the epididymal tubule, marked variations were detected at the protein level. BDKRB2 was highest in the efferent ducts and cauda epididymidis, intermediate in the distal initial segment, moderate in the corpus, and undetectable in the proximal initial segment and the caput. Functional assays on tubules isolated from the distal initial segments showed that BK significantly increased AQP9-dependent glycerol apical membrane permeability. This effect was inhibited by BAPTA-AM, demonstrating the participation of calcium in this process. This study, therefore, identifies BK as an important regulator of AQP9.
Figures





References
-
- Mukai H, Fitzgibbon WR, Bozeman G, Margolius HS, Ploth DW.Bradykinin B2 receptor antagonist increases chloride and water absorption in rat medullary collecting duct. Am J Physiol 1996; 271: R352–R360. - PubMed
-
- Rowland NE, Fregly MJ, Cimmerer AL.Bradykinin-induced water intake and brain fos-like immunoreactivity in rats. Brain Res 1995; 669: 73–78. - PubMed
-
- Bhoola KD, Figueroa CD, Worthy K.Bioregulation of kinins: kallikreins, kininogens, and kininases. Pharmacol Rev 1992; 44: 1–80. - PubMed
-
- Prado GN, Taylor L, Zhou X, Ricupero D, Mierke DF, Polgar P.Mechanisms regulating the expression, self-maintenance, and signaling-function of the bradykinin B2 and B1 receptors. J Cell Physiol 2002; 193: 275–286. - PubMed
-
- Leeb-Lundberg LM, Marceau F, Muller-Esterl W, Pettibone DJ, Zuraw BL.International union of pharmacology. XLV. Classification of the kinin receptor family: from molecular mechanisms to pathophysiological consequences. Pharmacol Rev 2005; 57: 27–77. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

