Testing the palindromic target site model for DNA transposon insertion using the Drosophila melanogaster P-element
- PMID: 18829720
- PMCID: PMC2577343
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkn563
Testing the palindromic target site model for DNA transposon insertion using the Drosophila melanogaster P-element
Abstract
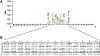
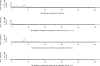
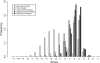
Understanding the molecular mechanisms that influence transposable element target site preferences is a fundamental challenge in functional and evolutionary genomics. Large-scale transposon insertion projects provide excellent material to study target site preferences in the absence of confounding effects of post-insertion evolutionary change. Growing evidence from a wide variety of prokaryotes and eukaryotes indicates that DNA transposons recognize staggered-cut palindromic target site motifs (TSMs). Here, we use over 10 000 accurately mapped P-element insertions in the Drosophila melanogaster genome to test predictions of the staggered-cut palindromic target site model for DNA transposon insertion. We provide evidence that the P-element targets a 14-bp palindromic motif that can be identified at the primary sequence level, which predicts the local spacing, hotspots and strand orientation of P-element insertions. Intriguingly, we find that the although P-element destroys the complete 14-bp target site upon insertion, the terminal three nucleotides of the P-element inverted repeats complement and restore the original TSM, suggesting a mechanistic link between transposon target sites and their terminal inverted repeats. Finally, we discuss how the staggered-cut palindromic target site model can be used to assess the accuracy of genome mappings for annotated P-element insertions.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Whole genome resequencing reveals natural target site preferences of transposable elements in Drosophila melanogaster.PLoS One. 2012;7(2):e30008. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0030008. Epub 2012 Feb 9. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22347367 Free PMC article.
-
Structural and sequence diversity of the transposon Galileo in the Drosophila willistoni genome.BMC Genomics. 2014 Sep 13;15(1):792. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-15-792. BMC Genomics. 2014. PMID: 25218200 Free PMC article.
-
Large-scale mapping of transposable element insertion sites using digital encoding of sample identity.Genetics. 2014 Mar;196(3):615-23. doi: 10.1534/genetics.113.159483. Epub 2013 Dec 27. Genetics. 2014. PMID: 24374352 Free PMC article.
-
Extra sequences found at P element excision sites in Drosophila melanogaster.Mol Gen Genet. 1992 Mar;232(1):17-23. doi: 10.1007/BF00299132. Mol Gen Genet. 1992. PMID: 1313147
-
Transposable elements as tools for genomics and genetics in Drosophila.Brief Funct Genomic Proteomic. 2003 Apr;2(1):57-71. doi: 10.1093/bfgp/2.1.57. Brief Funct Genomic Proteomic. 2003. PMID: 15239944 Review.
Cited by
-
P Transposable Elements in Drosophila and other Eukaryotic Organisms.Microbiol Spectr. 2015 Apr;3(2):MDNA3-0004-2014. doi: 10.1128/microbiolspec.MDNA3-0004-2014. Microbiol Spectr. 2015. PMID: 26104714 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Landscape of the DNA Transposons in the Genome of the Horezu_LaPeri Strain of Drosophila melanogaster.Insects. 2023 May 25;14(6):494. doi: 10.3390/insects14060494. Insects. 2023. PMID: 37367310 Free PMC article.
-
DNA Transposition at Work.Chem Rev. 2016 Oct 26;116(20):12758-12784. doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrev.6b00003. Epub 2016 May 17. Chem Rev. 2016. PMID: 27187082 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A divergent P element and its associated MITE, BuT5, generate chromosomal inversions and are widespread within the Drosophila repleta species group.Genome Biol Evol. 2013;5(6):1127-41. doi: 10.1093/gbe/evt076. Genome Biol Evol. 2013. PMID: 23682154 Free PMC article.
-
pLogo: a probabilistic approach to visualizing sequence motifs.Nat Methods. 2013 Dec;10(12):1211-2. doi: 10.1038/nmeth.2646. Epub 2013 Oct 6. Nat Methods. 2013. PMID: 24097270
References
-
- Craig NL. Mobile DNA II. Washington, DC: ASM Press; 2002.
-
- Hutchison CA, Peterson SN, Gill SR, Cline RT, White O, Fraser CM, Smith HO, Venter JC. Global transposon mutagenesis and a minimal Mycoplasma genome. Science. 1999;286:2165–2169. - PubMed
-
- Ross-Macdonald P, Coelho PS, Roemer T, Agarwal S, Kumar A, Jansen R, Cheung KH, Sheehan A, Symoniatis D, Umansky L, et al. Large-scale analysis of the yeast genome by transposon tagging and gene disruption. Nature. 1999;402:413–418. - PubMed
-
- Kuromori T, Hirayama T, Kiyosue Y, Takabe H, Mizukado S, Sakurai T, Akiyama K, Kamiya A, Ito T, Shinozaki K. A collection of 11 800 single-copy Ds transposon insertion lines in Arabidopsis. Plant J. 2004;37:897–905. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

