Inhibition of Na+/H+ exchanger enhances low pH-induced L-selectin shedding and beta2-integrin surface expression in human neutrophils
- PMID: 18829897
- PMCID: PMC2584992
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpcell.00535.2007
Inhibition of Na+/H+ exchanger enhances low pH-induced L-selectin shedding and beta2-integrin surface expression in human neutrophils
Abstract
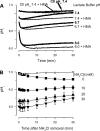
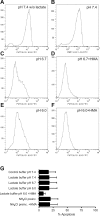
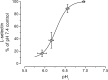
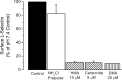
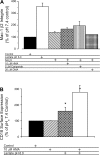
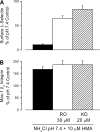
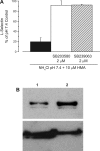
Ischemia-reperfusion injury is a common pathological occurrence causing tissue damage in heart attack and stroke. Entrapment of neutrophils in the vasculature during ischemic events has been implicated in this process. In this study, we examine the effects that lactacidosis and consequent reductions in intracellular pH (pH(i)) have on surface expression of adhesion molecules on neutrophils. When human neutrophils were exposed to pH 6 lactate, there was a marked decrease in surface L-selectin (CD62L) levels, and the decrease was significantly enhanced by inclusion of Na(+)/H(+) exchanger (NHE) inhibitor 5-(N,N-hexamethylene)amiloride (HMA). Similar effects were observed when pH(i) was reduced while maintaining normal extracellular pH, by using an NH(4)Cl prepulse followed by washes and incubation in pH 7.4 buffer containing NHE inhibitors [HMA, cariporide, or 5-(N,N-dimethyl)amiloride (DMA)]. The amount of L-selectin shedding induced by different concentrations of NH(4)Cl in the prepulse correlated with the level of intracellular acidification with an apparent pK of 6.3. In contrast, beta(2)-integrin (CD11b and CD18) was only slightly upregulated in the low-pH(i) condition and was enhanced by NHE inhibition to a much lesser extent. L-selectin shedding was prevented by treating human neutrophils with inhibitors of extracellular metalloproteases (RO-31-9790 and KD-IX-73-4) or with inhibitors of intracellular signaling via p38 MAP kinase (SB-203580 and SB-239063), implying a transmembrane effect of pH(i). Taken together, these data suggest that the ability of NHE inhibitors such as HMA to reduce ischemia-reperfusion injury may be related to the nearly complete removal of L-selectin from the neutrophil surface.
Figures
References
-
- Aronson PS, Suhm MA, Nee J. Interaction of external H+ with the Na+-H+ exchanger in renal microvillus membrane vesicles. J Biol Chem 258: 6767–6771, 1983. - PubMed
-
- Ayoub IM, Kolarova J, Yi Z, Trevedi A, Deshmukh H, Lubell DL, Franz MR, Maldonado FA, Gazmuri RJ. Sodium-hydrogen exchange inhibition during ventricular fibrillation: beneficial effects on ischemic contracture, action potential duration, reperfusion arrhythmias, myocardial function, and resuscitability. Circulation 107: 1804–1809, 2003. - PubMed
-
- Behmanesh S, Kempski O. Mechanisms of endothelial cell swelling from lactacidosis studied in vitro. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 279: H1512–H1517, 2000. - PubMed
-
- Berg EL, McEvoy LM, Berlin C, Bargatze RF, Butcher EC. L-selectin-mediated lymphocyte rolling on MAdCAM-1. Nature 366: 695–698, 1993. - PubMed
-
- Blobel CP ADAMs: key components in EGFR signalling and development. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 6: 32–43, 2005. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

