Drosophila painless is a Ca2+-requiring channel activated by noxious heat
- PMID: 18829951
- PMCID: PMC6671277
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2757-08.2008
Drosophila painless is a Ca2+-requiring channel activated by noxious heat
Abstract
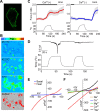
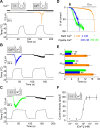
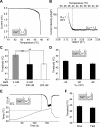
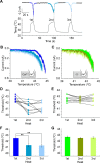
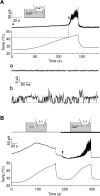
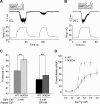
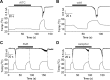
Thermal changes activate some members of the transient receptor potential (TRP) ion channel super family. They are primary sensors for detecting environmental temperatures. The Drosophila TRP channel Painless is believed responsible for avoidance of noxious heat because painless mutant flies display defects in heat sensing. However, no studies have proven its heat responsiveness. We show that Painless expressed in human embryonic kidney-derived 293 (HEK293) cells is a noxious heat-activated, Ca(2+)-permeable channel, and the function is mostly dependent on Ca(2+). In Ca(2+)-imaging, Painless mediated a robust intracellular Ca(2+) (Ca(2+)(i)) increase during heating, and it showed heat-evoked inward currents in whole-cell patch-clamp mode. Ca(2+) permeability was much higher than that of other cations. Heat-evoked currents were negligible in the absence of extracellular Ca(2+) (Ca(2+)(o)) and Ca(2+)(i), whereas 200 nm Ca(2+)(i) enabled heat activation of Painless. Activation kinetics were significantly accelerated in the presence of Ca(2+)(i). The temperature threshold for Painless activation was 42.6 degrees C in the presence of Ca(2+)(i), whereas the threshold was significantly increased to 44.1 degrees C when only Ca(2+)(o) was present. Temperature thresholds were further reduced after repetitive heating in a Ca(2+)-dependent manner. Ca(2+)-dependent heat activation of Painless was observed at the single-channel level in excised membranes. We found that a Ca(2+)-regulatory site is located in the N-terminal region of Painless. Painless-expressing HEK293 cells were insensitive to various thermosensitive TRP channel activators including allyl isothiocyanate, whereas mammalian TRPA1 inhibitors, ruthenium red, and camphor, reversibly blocked heat activation of Painless. Our results demonstrate that Painless is a direct sensor for noxious heat in Drosophila.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Molecular and functional characterization of a novel mouse transient receptor potential protein homologue TRP7. Ca(2+)-permeable cation channel that is constitutively activated and enhanced by stimulation of G protein-coupled receptor.J Biol Chem. 1999 Sep 24;274(39):27359-70. doi: 10.1074/jbc.274.39.27359. J Biol Chem. 1999. PMID: 10488066
-
Heat and AITC activate green anole TRPA1 in a membrane-delimited manner.Pflugers Arch. 2014 Oct;466(10):1873-84. doi: 10.1007/s00424-013-1420-z. Epub 2014 Jan 3. Pflugers Arch. 2014. PMID: 24385018
-
Requirement of extracellular Ca2+ binding to specific amino acids for heat-evoked activation of TRPA1.J Physiol. 2017 Apr 15;595(8):2451-2463. doi: 10.1113/JP274083. Epub 2017 Mar 22. J Physiol. 2017. PMID: 28194754 Free PMC article.
-
Transient receptor potential ion channels and animal sensation: lessons from Drosophila functional research.J Biochem Mol Biol. 2004 Jan 31;37(1):114-21. doi: 10.5483/bmbrep.2004.37.1.114. J Biochem Mol Biol. 2004. PMID: 14761309 Review.
-
The TRPC ion channels: association with Orai1 and STIM1 proteins and participation in capacitative and non-capacitative calcium entry.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2011;704:413-33. doi: 10.1007/978-94-007-0265-3_23. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2011. PMID: 21290309 Review.
Cited by
-
The ankyrin repeat domain of the TRPA protein painless is important for thermal nociception but not mechanical nociception.PLoS One. 2012;7(1):e30090. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0030090. Epub 2012 Jan 25. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22295071 Free PMC article.
-
TRPA channels distinguish gravity sensing from hearing in Johnston's organ.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009 Aug 11;106(32):13606-11. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0906377106. Epub 2009 Jul 28. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009. PMID: 19666538 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of Drosophila TRPA1 reveals an ancient origin for human chemical nociception.Nature. 2010 Mar 25;464(7288):597-600. doi: 10.1038/nature08848. Epub 2010 Mar 17. Nature. 2010. PMID: 20237474 Free PMC article.
-
Growing pains: development of the larval nocifensive response in Drosophila.Biol Bull. 2011 Dec;221(3):300-6. doi: 10.1086/BBLv221n3p300. Biol Bull. 2011. PMID: 22186918 Free PMC article.
-
The coding of temperature in the Drosophila brain.Cell. 2011 Feb 18;144(4):614-24. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2011.01.028. Cell. 2011. PMID: 21335241 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Al-Anzi B, Tracey WD, Jr, Benzer S. Response of Drosophila to wasabi is mediated by painless, the fly homolog of mammalian TRPA1/ANKTM1. Curr Biol. 2006;16:1034–1040. - PubMed
-
- Bautista DM, Jordt SE, Nikai T, Tsuruda PR, Read AJ, Poblete J, Yamoah EN, Basbaum AI, Julius D. TRPA1 mediates the inflammatory actions of environmental irritants and proalgesic agents. Cell. 2006;124:1269–1282. - PubMed
-
- Bautista DM, Siemens J, Glazer JM, Tsuruda PR, Basbaum AI, Stucky CL, Jordt SE, Julius D. The menthol receptor TRPM8 is the principal detector of environmental cold. Nature. 2007;448:204–208. - PubMed
-
- Caterina MJ. Transient receptor potential ion channels as participants in thermosensation and thermoregulation. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2007;292:R64–R76. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
