Inhibitory effects of Iranian Thymus vulgaris extracts on in vitro growth of Entamoeba histolytica
- PMID: 18830054
- PMCID: PMC2553340
- DOI: 10.3347/kjp.2008.46.3.153
Inhibitory effects of Iranian Thymus vulgaris extracts on in vitro growth of Entamoeba histolytica
Abstract
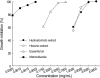
One of the most common drugs used against a wide variety of anaerobic protozoan parasites is metronidazole. However, this drug is mutagenic for bacteria and is a potent carcinogen for rodents. Thymus vulgaris is used for cough suppression and relief of dyspepsia. Also it has antibacterial and antifungal properties. The aim of this study was to investigate antiamebic effect of Thymus vulgaris against Entamoeba histolytica in comparison with metronidazole. One hundred gram air-dried T. vulgaris plant was obtained and macerated at 25 degrees C for 14 days using n-hexane and a mixture of ethanol and water. For essential oil isolation T. vulgaris was subjected to hydrodistillation using a clevenger-type apparatus for 3 hr. E. histolytica, HM-1: IMSS strain was used in all experiments. It was found that the minimal inhibitory concentration (MIC) for T. vulgaris hydroalcoholic, hexanic extracts, and the essential oil after 24 hr was 4 mg/mL, 4 mg/mL, and 0.7 mg/mL, respectively. After 48 hr the MIC for T. vulgaris hydroalcoholic and hexanic extracts was 3 and 3 mg/mL, respectively. Therefore, it can be concluded that the Iranian T. vulgaris is effective against the trophozoites of E. histolytica.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Activity of extracts and procesterol from Calotropis gigantea against Entamoeba histolytica.Nat Prod Commun. 2010 Jun;5(6):867-8. Nat Prod Commun. 2010. PMID: 20614811
-
Synergistic antibacterial activity between Thymus vulgaris and Pimpinella anisum essential oils and methanol extracts.J Ethnopharmacol. 2008 Mar 28;116(3):403-6. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2007.12.003. Epub 2007 Dec 14. J Ethnopharmacol. 2008. PMID: 18226481
-
In vitro susceptibility of Entamoeba histolytica and Giardia lamblia to plants used in Mexican traditional medicine for the treatment of gastrointestinal disorders.J Ethnopharmacol. 2006 Dec 6;108(3):367-70. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2006.05.025. Epub 2006 Jun 2. J Ethnopharmacol. 2006. PMID: 16846708
-
Drug resistance in amoebiasis.Indian J Med Res. 2006 Feb;123(2):115-8. Indian J Med Res. 2006. PMID: 16575108 Review.
-
Flavonoids as a Natural Treatment Against Entamoeba histolytica.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2018 Jun 22;8:209. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2018.00209. eCollection 2018. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2018. PMID: 29988403 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Polymeric nanoparticles for enhanced delivery and improved bioactivity of essential oils.Heliyon. 2023 Jun 2;9(6):e16543. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e16543. eCollection 2023 Jun. Heliyon. 2023. PMID: 37484246 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nanoparticle-Terpene Fusion: A Game-Changer in Combating Primary Amoebic Meningoencephalitis Caused by Naegleria fowleri.ACS Omega. 2024 Mar 1;9(10):11597-11607. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.3c08844. eCollection 2024 Mar 12. ACS Omega. 2024. PMID: 38497026 Free PMC article.
-
Investigation of the prophylactic and therapeutic effectiveness of oral thyme extract in rats experimentally infected with cryptosporidium parvum.Vet Res Commun. 2023 Jun;47(2):663-673. doi: 10.1007/s11259-022-10025-6. Epub 2022 Nov 3. Vet Res Commun. 2023. PMID: 36323839 Free PMC article.
-
Novel Formula of Antiprotozoal Mixtures.Antibiotics (Basel). 2022 Jul 7;11(7):913. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics11070913. Antibiotics (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35884167 Free PMC article.
-
Essential Oils as Novel Anthelmintic Drug Candidates.Molecules. 2022 Nov 29;27(23):8327. doi: 10.3390/molecules27238327. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 36500419 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- John DT, Petri WA., Jr . Markell and Voge's Medical Parasitology. 9th ed. USA: Saunders Elsevier; 2006. p. 23.
-
- Reed SL. Amebiasis and infection with free-living amebas. In: Harrison TR, Fauci AS, Braunwald E, editors. Harrison's Principles of Internal Medicine. 15th ed. New York, USA: McGraw-Hill; 2001. pp. 1199–1202.
-
- Petri WA, Jr, Singh U. Diagnosis and management of amebiasis. Clin Infect Dis. 1999;29:1117–1125. - PubMed
-
- Suwatana O. Acute diarrhea in under five-year-old children admitted to King Mongkut Prachomklao hospital Phetchaburi Province. J Med Assoc Thai. 1997;80:26–33. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

