Successful treatment of lupoid cutaneous leishmaniasis with glucantime and topical trichloroacetic acid (a case report)
- PMID: 18830058
- PMCID: PMC2553342
- DOI: 10.3347/kjp.2008.46.3.175
Successful treatment of lupoid cutaneous leishmaniasis with glucantime and topical trichloroacetic acid (a case report)
Abstract
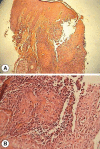
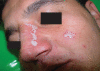
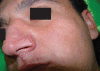
Lupoid leishmaniasis is a unique form of cutaneous leishmaniasis characterized by unusual clinical features and a chronic relapsing course, mostly caused by infection with Leishmania tropica. In this clinical form, 1-2 yr after healing of the acute lesion, new papules and nodules appear at the margin of the remaining scar. Herein, we describe a case of this clinical form that was resistant to 2 courses of treatments: systemic glucantime and then a combination therapy with allopurinol and systemic glucantime. However, marked improvement was seen after a combination therapy with topical trichloroacetic acid solution (50%) and systemic glucantime, and there were no signs of recurrence after 1 yr of follow-up.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Cutaneous lupoid leishmaniasis: a case report.Cutis. 2006 Jan;77(1):25-8; quiz 37-8. Cutis. 2006. PMID: 16475491
-
Comparison of lesion improvement in lupoid leishmaniasis patients with two treatment approaches: trichloroacetic Acid and intralesional meglumine antimoniate.J Cutan Med Surg. 2015 Jan-Feb;19(1):35-9. doi: 10.2310/7750.2014.13193. Epub 2015 Jan 1. J Cutan Med Surg. 2015. PMID: 25775661 Clinical Trial.
-
Efficacy of azithromycin versus systemic meglumine antimoniate (Glucantime) in the treatment of cutaneous leishmaniasis.Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2007 Jul;77(1):99-101. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2007. PMID: 17620637 Clinical Trial.
-
Systemic meglumine antimoniate in acute cutaneous leishmaniasis: children versus adults.Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2011 Apr;84(4):539-42. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.2011.10-0002. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2011. PMID: 21460006 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Effective meglumine antimoniate intralesional therapy for Chiclero's ulcer refractory to systemic liposomal amphotericin B.J Travel Med. 2021 Aug 27;28(6):taaa169. doi: 10.1093/jtm/taaa169. J Travel Med. 2021. PMID: 32918547 No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Synergic Effect of Allopurinol in Combination with Nitroheterocyclic Compounds against Trypanosoma cruzi.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2019 May 24;63(6):e02264-18. doi: 10.1128/AAC.02264-18. Print 2019 Jun. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2019. PMID: 30962342 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Asilian A, Iraji F, Hedaiti HR, Siadat AH, Enshaieh S. Carbon dioxide laser for the treatment of lupoid cutaneous leishmaniasis (LCL): a case series of 24 patients. Dermatol Online J. 2006;12:3. - PubMed
-
- Gurel MS, Ulukanligil M, Ozbilge H. Cutaneous leishmaniasis in Sanliurfa: epidemiologic and clinical features of the last four years (1997-2000) Int J Dermatol. 2002;41:32–37. - PubMed
-
- Nilfrousihzadeh MA, Jaffray F, Reiszadeh MR, Ansari N. The therapeutic effect of combined cryotherapy, paramomycin, and intralesional meglumine antimoniate in treating lupoid leishmaniasis and chronic leishmaniasis. Int J Dermatol. 2006;45:989–991. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

