Intraprotein electron transfer in inducible nitric oxide synthase holoenzyme
- PMID: 18830722
- PMCID: PMC2596912
- DOI: 10.1007/s00775-008-0431-2
Intraprotein electron transfer in inducible nitric oxide synthase holoenzyme
Abstract
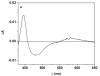
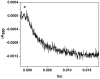
Intraprotein electron transfer (IET) from flavin mononucleotide (FMN) to heme is essential in NO synthesis by NO synthase (NOS). Our previous laser flash photolysis studies provided a direct determination of the kinetics of the FMN-heme IET in a truncated two-domain construct (oxyFMN) of murine inducible NOS (iNOS), in which only the oxygenase and FMN domains along with the calmodulin (CaM) binding site are present (Feng et al. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 128, 3808-3811, 2006). Here we report the kinetics of the IET in a human iNOS oxyFMN construct, a human iNOS holoenzyme, and a murine iNOS holoenzyme, using CO photolysis in comparative studies on partially reduced NOS and a NOS oxygenase construct that lacks the FMN domain. The IET rate constants for the human and murine iNOS holoenzymes are 34 +/- 5 and 35 +/- 3 s(-1), respectively, thereby providing a direct measurement of this IET between the catalytically significant redox couples of FMN and heme in the iNOS holoenzyme. These values are approximately an order of magnitude smaller than that in the corresponding iNOS oxyFMN construct, suggesting that in the holoenzyme the rate-limiting step in the IET is the conversion of the shielded electron-accepting (input) state to a new electron-donating (output) state. The fact that there is no rapid IET component in the kinetic traces obtained with the iNOS holoenzyme implies that the enzyme remains mainly in the input state. The IET rate constant value for the iNOS holoenzyme is similar to that obtained for a CaM-bound neuronal NOS holoenzyme, suggesting that CaM activation effectively removes the inhibitory effect of the unique autoregulatory insert in neuronal NOS.
Figures








Similar articles
-
Direct measurement by laser flash photolysis of intraprotein electron transfer in a rat neuronal nitric oxide synthase.J Am Chem Soc. 2007 May 2;129(17):5621-9. doi: 10.1021/ja068685b. Epub 2007 Apr 11. J Am Chem Soc. 2007. PMID: 17425311
-
Intraprotein electron transfer in a two-domain construct of neuronal nitric oxide synthase: the output state in nitric oxide formation.Biochemistry. 2006 May 23;45(20):6354-62. doi: 10.1021/bi060223n. Biochemistry. 2006. PMID: 16700546
-
Intraprotein electron transfer between the FMN and heme domains in endothelial nitric oxide synthase holoenzyme.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2011 Dec;1814(12):1997-2002. doi: 10.1016/j.bbapap.2011.08.004. Epub 2011 Aug 16. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2011. PMID: 21864726 Free PMC article.
-
Dissecting regulation mechanism of the FMN to heme interdomain electron transfer in nitric oxide synthases.J Inorg Biochem. 2014 Jan;130:130-40. doi: 10.1016/j.jinorgbio.2013.09.005. Epub 2013 Sep 13. J Inorg Biochem. 2014. PMID: 24084585 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[Mechanisms of regulation by calmodulin of nitric oxide synthase].Vopr Med Khim. 1999 May-Jun;45(3):187-99. Vopr Med Khim. 1999. PMID: 10432553 Review. Russian.
Cited by
-
A docked state conformational dynamics model to explain the ionic strength dependence of FMN - heme electron transfer in nitric oxide synthase.J Inorg Biochem. 2018 Jul;184:146-155. doi: 10.1016/j.jinorgbio.2018.03.012. Epub 2018 Mar 26. J Inorg Biochem. 2018. PMID: 29751215 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of solution viscosity on intraprotein electron transfer between the FMN and heme domains in inducible nitric oxide synthase.FEBS Lett. 2011 Aug 19;585(16):2622-6. doi: 10.1016/j.febslet.2011.07.022. Epub 2011 Jul 26. FEBS Lett. 2011. PMID: 21803041 Free PMC article.
-
Comparing the temperature dependence of FMN to heme electron transfer in full length and truncated inducible nitric oxide synthase proteins.FEBS Lett. 2012 Jan 20;586(2):159-62. doi: 10.1016/j.febslet.2011.12.009. Epub 2011 Dec 17. FEBS Lett. 2012. PMID: 22198200 Free PMC article.
-
Role of an isoform-specific serine residue in FMN-heme electron transfer in inducible nitric oxide synthase.J Biol Inorg Chem. 2012 Jun;17(5):675-85. doi: 10.1007/s00775-012-0887-y. Epub 2012 Mar 10. J Biol Inorg Chem. 2012. PMID: 22407542 Free PMC article.
-
Mutation in the flavin mononucleotide domain modulates magnetic circular dichroism spectra of the iNOS ferric cyano complex in a substrate-specific manner.Inorg Chem. 2011 Aug 1;50(15):6859-61. doi: 10.1021/ic200952c. Epub 2011 Jun 30. Inorg Chem. 2011. PMID: 21718007 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

