Promoter-sharing by different genes in human genome--CPNE1 and RBM12 gene pair as an example
- PMID: 18831769
- PMCID: PMC2568002
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2164-9-456
Promoter-sharing by different genes in human genome--CPNE1 and RBM12 gene pair as an example
Abstract
Background: Regulation of gene expression plays important role in cellular functions. Co-regulation of different genes may indicate functional connection or even physical interaction between gene products. Thus analysis on genomic structures that may affect gene expression regulation could shed light on the functions of genes.
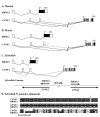
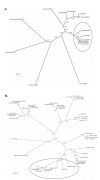
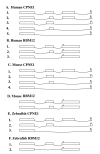
Results: In a whole genome analysis of alternative splicing events, we found that two distinct genes, copine I (CPNE1) and RNA binding motif protein 12 (RBM12), share the most 5' exons and therefore the promoter region in human. Further analysis identified many gene pairs in human genome that share the same promoters and 5' exons but have totally different coding sequences. Analysis of genomic and expressed sequences, either cDNAs or expressed sequence tags (ESTs) for CPNE1 and RBM12, confirmed the conservation of this phenomenon during evolutionary courses. The co-expression of the two genes initiated from the same promoter is confirmed by Reverse Transcription-Polymerase Chain Reaction (RT-PCR) in different tissues in both human and mouse. High degrees of sequence conservation among multiple species in the 5'UTR region common to CPNE1 and RBM12 were also identified.
Conclusion: Promoter and 5'UTR sharing between CPNE1 and RBM12 is observed in human, mouse and zebrafish. Conservation of this genomic structure in evolutionary courses indicates potential functional interaction between the two genes. More than 20 other gene pairs in human genome were found to have the similar genomic structure in a genome-wide analysis, and it may represent a unique pattern of genomic arrangement that may affect expression regulation of the corresponding genes.
Figures


References
-
- Zhang W, Morris QD, Chang R, Shai O, Bakowski MA, Mitsakakis N, Mohammad N, Robinson MD, Zirngibl R, Somogyi E, Laurin N, Eftekharpour E, Sat E, Grigull J, Pan Q, Peng WT, Krogan N, Greenblatt J, Fehlings M, Kooy D van der, Aubin J, Bruneau BG, Rossant J, Blencowe BJ, Frey BJ, Hughes TR. The functional landscape of mouse gene expression. J Biol. 2004;3:21. doi: 10.1186/jbiol16. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

