Short Linear Motifs recognized by SH2, SH3 and Ser/Thr Kinase domains are conserved in disordered protein regions
- PMID: 18831792
- PMCID: PMC2559891
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2164-9-S2-S26
Short Linear Motifs recognized by SH2, SH3 and Ser/Thr Kinase domains are conserved in disordered protein regions
Abstract
Background: Protein interactions are essential for most cellular functions. Interactions mediated by domains that appear in a large number of proteins are of particular interest since they are expected to have an impact on diversities of cellular processes such as signal transduction and immune response. Many well represented domains recognize and bind to primary sequences less than 10 amino acids in length called Short Linear Motifs (SLiMs).
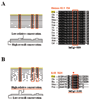
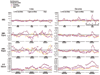
Results: In this study, we systematically studied the evolutionary conservation of SLiMs recognized by SH2, SH3 and Ser/Thr Kinase domains in both ordered and disordered protein regions. Disordered protein regions are protein sequences that lack a fixed three-dimensional structure under putatively native conditions. We find that, in all these domains examined, SLiMs are more conserved in disordered regions. This trend is more evident in those protein functional groups that are frequently reported to interact with specific domains.
Conclusion: The correlation between SLiM conservation with disorder prediction demonstrates that functional SLiMs recognized by each domain occur more often in disordered as compared to structured regions of proteins.
Figures

References
-
- Puntervoll P, Linding R, Gemund C, Chabanis-Davidson S, Mattingsdal M, Cameron S, Martin DM, Ausiello G, Brannetti B, Costantini A, et al. ELM server: A new resource for investigating short functional sites in modular eukaryotic proteins. Nucleic Acids Res. 2003;31:3625–3630. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkg545. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

