HBO1 histone acetylase is a coactivator of the replication licensing factor Cdt1
- PMID: 18832067
- PMCID: PMC2559906
- DOI: 10.1101/gad.1674108
HBO1 histone acetylase is a coactivator of the replication licensing factor Cdt1
Abstract
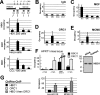
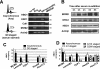
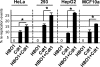
HBO1 histone acetylase is important for DNA replication licensing. In human cells, HBO1 associates with replication origins specifically during the G1 phase of the cell cycle in a manner that depends on the replication licensing factor Cdt1, but is independent of the Cdt1 repressor Geminin. HBO1 directly interacts with Cdt1, and it enhances Cdt1-dependent rereplication. Thus, HBO1 plays a direct role at replication origins as a coactivator of the Cdt1 licensing factor. As HBO1 is also a transcriptional coactivator, it has the potential to integrate internal and external stimuli to coordinate transcriptional responses with initiation of DNA replication.
Figures


References
-
- Aggarwal B.D., Calvi B.R. Chromatin regulates origin activity in Drosophila follicle cells. Nature. 2004;430:372–376. - PubMed
-
- Arias E.E., Walter J.C. Strength in numbers: Preventing rereplication via multiple mechanisms in eukaryotic cells. Genes & Dev. 2007;21:497–518. - PubMed
-
- Bell S.P., Dutta A. DNA replication in eukaryotic cells. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2002;71:333–374. - PubMed
-
- Burke T.W., Cook J.G., Asano M., Nevins J.R. Replication factors MCM2 and ORC1 interact with the histone acetyltransferase HBO1. J. Biol. Chem. 2001;276:15397–15408. - PubMed
-
- Cawley S., Bekiranov S., Ng H.H., Kapranov P., Sekinger E.A., Kampa D., Piccolboni A., Sementchenko V., Cheng J., Williams A.J., et al. Unbiased mapping of transcription factor binding sites along human chromosomes 21 and 22 points to widespread regulation of noncoding RNAs. Cell. 2004;116:499–509. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
