Identification of Staphylococcus spp. by PCR-restriction fragment length polymorphism analysis of dnaJ gene
- PMID: 18832127
- PMCID: PMC2593281
- DOI: 10.1128/JCM.00810-08
Identification of Staphylococcus spp. by PCR-restriction fragment length polymorphism analysis of dnaJ gene
Abstract
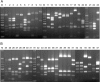
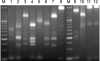
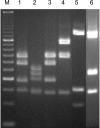
A PCR-restriction fragment length polymorphism (RFLP) analysis method that analyzes a part of the dnaJ gene was designed for the rapid and accurate identification of Staphylococcus spp. XapI or Bsp143I digestion of the PCR-generated products rendered distinctive RFLP patterns that allowed 41 reference species and subspecies to be identified with a high degree of specificity. The novel method was validated by the identification of 23 clinical staphylococcal strains, and the results were compared with those obtained by other genotypic identification methods. A 100% concordance of the results was shown. Therefore, PCR-RFLP analysis of the dnaJ gene is proposed as a reliable and reproducible method for the identification of Staphylococcus spp.
Figures
References
-
- Barros, E. M., N. L. Iório, C. Bastos Mdo, K. R. dos Santos, and M. Giambiagi-deMarval. 2007. Species-level identification of clinical staphylococcal isolates based on polymerase chain reaction-restriction fragment length polymorphism analysis of a partial groEL gene sequence. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 59251-257. - PubMed
-
- Cirkovic, I., S. Stepanovic, D. Vukovic, M. Svabic-Vlahovic, V. Dimitrijeviæ, and T. Hauschild. 2008. Evaluation of the BD Phoenix automated microbiology system for detecting methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 3294-95. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

