A procedure for highly specific, sensitive, and unbiased whole-genome amplification
- PMID: 18832167
- PMCID: PMC2563063
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0808028105
A procedure for highly specific, sensitive, and unbiased whole-genome amplification
Abstract
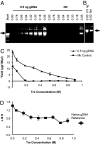
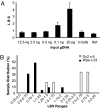
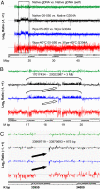
Highly specific amplification of complex DNA pools without bias or template-independent products (TIPs) remains a challenge. We have developed a method using phi29 DNA polymerase and trehalose and optimized control of amplification to create micrograms of specific amplicons without TIPs from down to subfemtograms of DNA. With an input of as little as 0.5-2.5 ng of human gDNA or a few cells, the product could be close to native DNA in locus representation. The amplicons from 5 and 0.5 ng of DNA faithfully demonstrated all previously known heterozygous segmental duplications and deletions (3 Mb to 18 kb) located on chromosome 22 and even a homozygous deletion smaller than 1 kb with high-resolution chromosome-wide comparative genomic hybridization. With 550k Infinium BeadChip SNP typing, the >99.7% accuracy was compared favorably with results on unamplified DNA. Importantly, underrepresentation of chromosome termini that occurred with GenomiPhi v2 was greatly rescued with the present procedure, and the call rate and accuracy of SNP typing were also improved for the amplicons with a 0.5-ng, partially degraded DNA input. In addition, the amplification proceeded logarithmically in terms of total yield before saturation; the intact cells was amplified >50 times more efficiently than an equivalent amount of extracted DNA; and the locus imbalance for amplicons with 0.1 ng or lower input of DNA was variable, whereas for higher input it was largely reproducible. This procedure facilitates genomic analysis with single cells or other traces of DNA, and generates products suitable for analysis by massively parallel sequencing as well as microarray hybridization.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
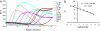
Similar articles
-
Evaluation of Phi29-based whole-genome amplification for microarray-based comparative genomic hybridisation.Lab Invest. 2007 Jan;87(1):75-83. doi: 10.1038/labinvest.3700495. Lab Invest. 2007. PMID: 17170740
-
Balanced-PCR amplification allows unbiased identification of genomic copy changes in minute cell and tissue samples.Nucleic Acids Res. 2004 May 21;32(9):e76. doi: 10.1093/nar/gnh070. Nucleic Acids Res. 2004. PMID: 15155823 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of DNA mass on multiple displacement whole genome amplification and genotyping performance.BMC Biotechnol. 2005 Sep 16;5:24. doi: 10.1186/1472-6750-5-24. BMC Biotechnol. 2005. PMID: 16168060 Free PMC article.
-
An isothermal primer extension method for whole genome amplification of fresh and degraded DNA: applications in comparative genomic hybridization, genotyping and mutation screening.Nat Protoc. 2006;1(5):2185-94. doi: 10.1038/nprot.2006.398. Nat Protoc. 2006. PMID: 17406456
-
Multiple displacement amplification to create a long-lasting source of DNA for genetic studies.Hum Mutat. 2006 Jul;27(7):603-14. doi: 10.1002/humu.20341. Hum Mutat. 2006. PMID: 16786504 Review.
Cited by
-
How to open the treasure chest? Optimising DNA extraction from herbarium specimens.PLoS One. 2012;7(8):e43808. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0043808. Epub 2012 Aug 28. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22952770 Free PMC article.
-
Single-Cell Genetic Analysis Using Automated Microfluidics to Resolve Somatic Mosaicism.PLoS One. 2015 Aug 24;10(8):e0135007. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0135007. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26302375 Free PMC article.
-
Artifactual pyrosequencing reads in multiple-displacement-amplified sediment metagenomes from the Red Sea.PeerJ. 2013 Apr 30;1:e69. doi: 10.7717/peerj.69. Print 2013. PeerJ. 2013. PMID: 23646288 Free PMC article.
-
Nearly finished genomes produced using gel microdroplet culturing reveal substantial intraspecies genomic diversity within the human microbiome.Genome Res. 2013 May;23(5):878-88. doi: 10.1101/gr.142208.112. Epub 2013 Mar 14. Genome Res. 2013. PMID: 23493677 Free PMC article.
-
Single nucleotide polymorphism discovery in rainbow trout by deep sequencing of a reduced representation library.BMC Genomics. 2009 Nov 25;10:559. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-10-559. BMC Genomics. 2009. PMID: 19939274 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hutchison CA, III, Venter JC. Single-cell genomics. Nat Biotechnol. 2006;24:657–658. - PubMed
-
- Lasken RS. Single-cell genomic sequencing using multiple displacement amplification. Curr Opin Microbiol. 2007;10:510–516. - PubMed
-
- Hughes S, Arneson N, Done S, Squire J. The use of whole genome amplification in the study of human disease. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 2005;88:173–189. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

