Interleukin-10 promotes Mycobacterium tuberculosis disease progression in CBA/J mice
- PMID: 18832712
- PMCID: PMC2728584
- DOI: 10.4049/jimmunol.181.8.5545
Interleukin-10 promotes Mycobacterium tuberculosis disease progression in CBA/J mice
Abstract
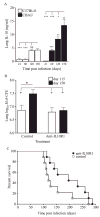
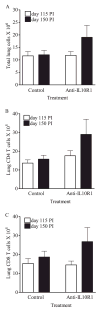
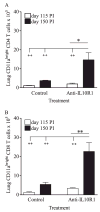
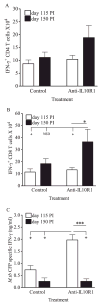
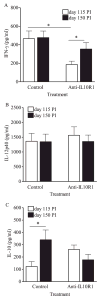
IL-10 is a potent immunomodulatory cytokine that affects innate and acquired immune responses. The immunological consequences of IL-10 production during pulmonary tuberculosis (TB) are currently unknown, although IL-10 has been implicated in reactivation TB in humans and with TB disease in mice. Using Mycobacterium tuberculosis-susceptible CBA/J mice, we show that blocking the action of IL-10 in vivo during chronic infection stabilized the pulmonary bacterial load and improved survival. Furthermore, this beneficial outcome was highly associated with the recruitment of T cells to the lungs and enhanced T cell IFN-gamma production. Our results indicate that IL-10 promotes TB disease progression. These findings have important diagnostic and/or therapeutic implications for the prevention of reactivation TB in humans.
Figures
References
-
- Moore KW, de Waal Malefyt R, Coffman RL, O’Garra A. Interleukin-10 and the interleukin-10 receptor. Annu Rev Immunol. 2001;19:683–765. - PubMed
-
- Fiorentino D, Zlotnik A, Mosmann T, Howard M, O’Garra A. IL-10 inhibits cytokine production by activated macrophages. J Immunol. 1991;147:3815–3222. - PubMed
-
- Koppelman B, Neefjes JJ, de Vries JE, de Waal Malefyt R. Interleukin-10 down-regulates MHC class II alphabeta peptide complexes at the plasma membrane of monocytes by affecting arrival and recycling. Immunity. 1997;7:861– 871. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

