Sites of distant recurrence and clinical outcomes in patients with metastatic triple-negative breast cancer: high incidence of central nervous system metastases
- PMID: 18833576
- PMCID: PMC2835546
- DOI: 10.1002/cncr.23930
Sites of distant recurrence and clinical outcomes in patients with metastatic triple-negative breast cancer: high incidence of central nervous system metastases
Abstract
Background: The purpose of the current study was to characterize the outcomes of patients with metastatic triple-negative breast cancers, including the risk and clinical consequences of central nervous system (CNS) recurrence.
Methods: Using pharmacy and pathology records, a study group of 116 patients who were treated for metastatic triple-negative breast cancer at Dana-Farber Cancer Institute between January 2000 and June 2006 was identified.
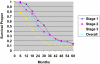
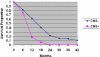
Results: The median survival from time of metastatic diagnosis was 13.3 months. Sixteen patients (14%) were diagnosed with CNS involvement at the time of initial metastatic diagnosis; overall, 46% of patients were diagnosed with CNS metastases before death. The median survival after a diagnosis of CNS metastasis was 4.9 months. The age-adjusted and race-adjusted rate of death for patients whose first presentation included a CNS metastasis was 3.4 times (95% confidence interval, 1.9-6.1 times) that of patients without a CNS lesion at the time of first metastatic presentation. Of the 53 patients who developed brain metastases, only 3 patients were judged to have stable or responsive systemic disease in the face of progressive CNS disease at the last follow-up before death.
Conclusions: Triple-negative breast cancer is associated with poor survival after recurrence. CNS recurrence is common, but death as a direct consequence of CNS progression in the setting of controlled systemic disease is uncommon. Thus, it does not appear that the high rate of CNS involvement is because of a sanctuary effect, but rather is due to the lack of effective therapies in general for this aggressive subtype of breast cancer. New treatment strategies are needed.
Figures
References
-
- Perou CM, Sorlie T, Eisen MB, et al. Molecular portraits of human breast tumours. Nature. 2000;406:747–52. - PubMed
-
- Nielsen TO, Hsu FD, Jensen K, et al. Immunohistochemical and clinical characterization of the basal-like subtype of invasive breast carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res. 2004;10:5367–74. - PubMed
-
- Foulkes WD, Brunet JS, Stefansson IM, et al. The prognostic implication of the basal-like (cyclin E high/p27 low/p53+/glomeruloid-microvascular-proliferation+) phenotype of BRCA1-related breast cancer. Cancer Res. 2004;64:830–5. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous