Protracted CRP elevation after atrial fibrillation ablation
- PMID: 18834466
- PMCID: PMC2596767
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1540-8159.2008.01155.x
Protracted CRP elevation after atrial fibrillation ablation
Abstract
Background: Atrial fibrillation (AF) has been linked to an inflammatory process detected through various biomarkers, including C-Reactive Protein (CRP). Early recurrence of AF within the first 3 months after curative AF ablation is not felt to reflect success or failure of the procedure. We hypothesized that this early recurrence is due to an inflammatory response to the ablation itself. We therefore sought to evaluate levels of CRP after AF ablation.
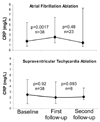
Methods: We prospectively enrolled subjects undergoing AF ablation. A control group of patients undergoing ablation for supraventricular tachycardia (SVT) was also enrolled. Each patient had CRP drawn on the day of the procedure (prior to ablation) and during their first follow-up (median 49 days, interquartile range [IQR] 37-93) and second follow-up (median 147 days, IQR 141-257) clinic visits. Patient interviews were performed and medical histories reviewed for evidence of recurrent AF prior to the first follow-up.
Results: CRP levels significantly increased from baseline to first follow-up in the AF ablation group (P = 0.0017). CRP did not significantly change after SVT ablation (P = 0.92). Seventeen (45%) of the AF subjects exhibited recurrence of AF prior to first follow-up. After adjusting for multiple potential confounders, AF ablation patients with recurrent AF prior to their first follow-up had a statistically significant greater odds of having an increase in CRP (OR 21, 95% CI 1.1-417, P = 0.045).
Conclusions: AF ablation generates an inflammatory response that persists for several weeks. This inflammation may explain early recurrence of AF after curative ablation.
Conflict of interest statement
Author disclosures/ potential conflicts of interest: None
Figures

References
-
- Calkins H, Brugada J, Packer DL, Cappato R, Chen SA, Crijns HJ, Damiano RJ, et al. HRS/EHRA/ECAS expert consensus statement on catheter and surgical ablation of atrial fibrillation: recommendations for personnel, policy, procedures and follow-up. Europace. 2007;9(6):335–379. - PubMed
-
- Oral H, Knight BP, Ozaydin M, Tada H, Chugh A, Hassan S, Scharf C, et al. Clinical significance of early recurrences of atrial fibrillation after pulmonary vein isolation. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2002;40(1):100–104. - PubMed
-
- Bertaglia E, Stabile G, Senatore G, Zoppo F, Turco P, Amellone C, De Simone A, et al. Predictive value of early atrial tachyarrhythmias recurrence after circumferential anatomical pulmonary vein ablation. PACE. 2005;28(5):366–371. - PubMed
-
- Jiang H, Lu Z, Lei H, Zhao D, Yang B, Huang C. Predictors of early recurrence and delayed cure after segmental pulmonary vein isolation for paroxysmal atrial fibrillation without structural heart disease. J Interventional Cardiac Electrophysiol. 2006;15(3):157–163. - PubMed
-
- Lee SH, Tai CT, Hsieh MH, Tsai CF, Lin YK, Tsao HM, Yu WC, et al. Predictors of early and late recurrence of atrial fibrillation after catheter ablation of paroxysmal atrial fibrillation. J Interventional Cardiac Electrophysiol. 2004;10(3):221–226. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

