Osr1 expression demarcates a multi-potent population of intermediate mesoderm that undergoes progressive restriction to an Osr1-dependent nephron progenitor compartment within the mammalian kidney
- PMID: 18835385
- PMCID: PMC2642884
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2008.09.010
Osr1 expression demarcates a multi-potent population of intermediate mesoderm that undergoes progressive restriction to an Osr1-dependent nephron progenitor compartment within the mammalian kidney
Abstract
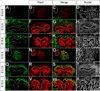
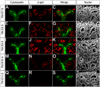
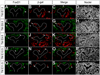
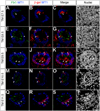
The mammalian metanephric kidney is derived from the intermediate mesoderm. In this report, we use molecular fate mapping to demonstrate that the majority of cell types within the metanephric kidney arise from an Osr1(+) population of metanephric progenitor cells. These include the ureteric epithelium of the collecting duct network, the cap mesenchyme and its nephron epithelia derivatives, the interstitial mesenchyme, vasculature and smooth muscle. Temporal fate mapping shows a progressive restriction of Osr1(+) cell fates such that at the onset of active nephrogenesis, Osr1 activity is restricted to the Six2(+) cap mesenchyme nephron progenitors. However, low-level labeling of Osr1(+) cells suggests that the specification of interstitial mesenchyme and cap mesenchyme progenitors occurs within the Osr1(+) population prior to the onset of metanephric development. Furthermore, although Osr1(+) progenitors give rise to much of the kidney, Osr1 function is only essential for the development of the nephron progenitor compartment. These studies provide new insights into the cellular origins of metanephric kidney structures and lend support to a model where Osr1 function is limited to establishing the nephron progenitor pool.
Figures



References
-
- Bernstein J, Cheng F, Roszka J. Glomerular differentiation in metanephric culture. Lab Invest. 1981;45:183–190. - PubMed
-
- Boyle S, Misfeldt A, Chandler KJ, Deal KK, Southard-Smith EM, Mortlock DP, Baldwin HS, de Caestecker M. Fate mapping using Cited1-CreERT2 mice demonstrates that the cap mesenchyme contains self-renewing progenitor cells and gives rise exclusively to nephronic epithelia. Dev Biol. 2008;313:234–245. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Carroll TJ, Park JS, Hayashi S, Majumdar A, McMahon AP. Wnt9b plays a central role in the regulation of mesenchymal to epithelial transitions underlying organogenesis of the mammalian urogenital system. Dev Cell. 2005;9:283–292. - PubMed
-
- Challen GA, Bertoncello I, Deane JA, Ricardo SD, Little MH. Kidney side population reveals multilineage potential and renal functional capacity but also cellular heterogeneity. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2006;17:1896–1912. - PubMed
-
- Costantini F. Renal branching morphogenesis: concepts, questions, and recent advances. Differentiation. 2006;74:402–421. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

