CCN family 2/connective tissue growth factor (CCN2/CTGF) regulates the expression of Vegf through Hif-1alpha expression in a chondrocytic cell line, HCS-2/8, under hypoxic condition
- PMID: 18835464
- PMCID: PMC2760594
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bone.2008.08.125
CCN family 2/connective tissue growth factor (CCN2/CTGF) regulates the expression of Vegf through Hif-1alpha expression in a chondrocytic cell line, HCS-2/8, under hypoxic condition
Abstract
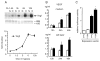
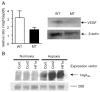
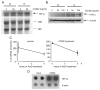
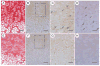
Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) is essential for establishing vascularization and regulating chondrocyte development and survival. We have demonstrated that VEGF regulates the expression of CCN2/connective tissue growth factor (CCN2/CTGF) an essential mediator of cartilage development and angiogenesis, suggesting that CCN2 functions in down-stream of VEGF, and that VEGF function is mediated in part by CCN2. On the other hand, the phenotype of Ccn2 mutant growth plates, which exhibit decreased expression of VEGF in the hypertrophic zone, indicates that Vegf expression is dependent on Ccn2 expression as well. Therefore, we investigated the molecular mechanisms underlying the induction of VEGF by CCN2 using a human chondrocytic cell line, HCS-2/8. Hypoxic stimulation (5% O(2)) of HCS-2/8 cells increased VEGF mRNA levels by approximately 8 fold within 6 h as compared with the cells cultured under normoxia. In addition, VEGF expression was further up-regulated under hypoxia in HCS-2/8 cells transfected with a Ccn2 expression plasmid. Hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF)-1alpha mRNA and protein levels were increased by stimulation with recombinant CCN2 (rCCN2). Furthermore, the activity of a VEGF promoter that contained a HIF-1 binding site was increased in HCS-2/8, when the cells were stimulated by rCCN2. These results suggest that CCN2 regulates the expression of VEGF at a transcriptional level by promoting HIF-1alpha activity. In fact, HIF-1alpha was detected in the nuclei of proliferative and pre-hypertrophic chondrocytes of wild-type mice, whereas it was not detected in Ccn2 mutant chondrocytes in vivo. This activation cascade from CCN2 to VEGF may therefore play a critical role in chondrocyte development and survival.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF)-1α and CCN2 form a regulatory circuit in hypoxic nucleus pulposus cells: CCN2 suppresses HIF-1α level and transcriptional activity.J Biol Chem. 2013 May 3;288(18):12654-66. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.448860. Epub 2013 Mar 24. J Biol Chem. 2013. PMID: 23530034 Free PMC article.
-
Oxygen tension regulates the expression of ANK (progressive ankylosis) in an HIF-1-dependent manner in growth plate chondrocytes.J Bone Miner Res. 2009 Nov;24(11):1869-78. doi: 10.1359/jbmr.090512. J Bone Miner Res. 2009. PMID: 19419319 Free PMC article.
-
HIF-1α/GPER signaling mediates the expression of VEGF induced by hypoxia in breast cancer associated fibroblasts (CAFs).Breast Cancer Res. 2013;15(4):R64. doi: 10.1186/bcr3458. Breast Cancer Res. 2013. PMID: 23947803 Free PMC article.
-
Posttranslational modifications of collagens as targets of hypoxia and Hif-1alpha in endochondral bone development.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2010 Mar;1192:317-21. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.2009.05236.x. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2010. PMID: 20392253 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Connective tissue growth factor (CCN2) in blood vessels.Vascul Pharmacol. 2013 Mar;58(3):189-93. doi: 10.1016/j.vph.2013.01.004. Epub 2013 Feb 4. Vascul Pharmacol. 2013. PMID: 23380714 Review.
Cited by
-
CCN proteins in the musculoskeletal system: current understanding and challenges in physiology and pathology.J Cell Commun Signal. 2021 Dec;15(4):545-566. doi: 10.1007/s12079-021-00631-5. Epub 2021 Jul 6. J Cell Commun Signal. 2021. PMID: 34228239 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Investigating microenvironmental regulation of human chordoma cell behaviour.PLoS One. 2014 Dec 26;9(12):e115909. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0115909. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25541962 Free PMC article.
-
In Vitro Identification of New Transcriptomic and miRNomic Profiles Associated with Pulmonary Fibrosis Induced by High Doses Everolimus: Looking for New Pathogenetic Markers and Therapeutic Targets.Int J Mol Sci. 2018 Apr 20;19(4):1250. doi: 10.3390/ijms19041250. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 29677166 Free PMC article.
-
Rescue of murine hind limb ischemia via angiogenesis and lymphangiogenesis promoted by cellular communication network factor 2.Sci Rep. 2023 Nov 16;13(1):20029. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-47485-y. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 37973852 Free PMC article.
-
"A small leak will sink a great ship": hypoxia-inducible factor and group III pulmonary hypertension.Receptors Clin Investig. 2016;3(1):e1213. doi: 10.14800/rci.1213. Epub 2016 Mar 14. Receptors Clin Investig. 2016. PMID: 27446973 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Zelzer E, Olsen BR. The genetic basis for skeletal diseases. Nature. 2003;423:343–8. - PubMed
-
- Perbal B, Takigawa M. The CCN family of proteins: an overview. In: Perbal B, Takigawa M, editors. CCN proteins: a new family of cell growth and differentiation regulators. London: Imperial College Press; 2005. pp. 1–18.
-
- Takigawa M. CTGF/Hcs24 as a multifunctional growth factor for fibroblasts, chondrocytes and vascular endothelial cells. Drug News Perspect. 2003;16:11–21. - PubMed
-
- Perbal B. CCN proteins: multifunctional signalling regulators. Lancet. 2004;363:62–4. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

