Lysyl oxidase binds transforming growth factor-beta and regulates its signaling via amine oxidase activity
- PMID: 18835815
- PMCID: PMC2590693
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M803142200
Lysyl oxidase binds transforming growth factor-beta and regulates its signaling via amine oxidase activity
Abstract
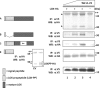
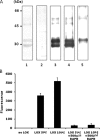
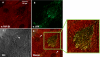
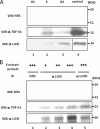
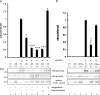
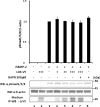
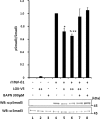
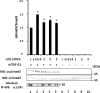
Lysyl oxidase (LOX), an amine oxidase critical for the initiation of collagen and elastin cross-linking, has recently been shown to regulate cellular activities possibly by modulating the functions of growth factors. In this study, we investigated the interaction between LOX and transforming growth factor-beta1 (TGF-beta1), a potent growth factor abundant in bone, the effect of LOX on TGF-beta1 signaling, and its potential mechanism. The specific binding between mature LOX and mature TGF-beta1 was demonstrated by immunoprecipitation and glutathione S-transferase pulldown assay in vitro. Both proteins were colocalized in the extracellular matrix in an osteoblastic cell culture system, and the binding complex was identified in the mineral-associated fraction of bone matrix. Furthermore, LOX suppressed TGF-beta1-induced Smad3 phosphorylation likely through its amine oxidase activity. The data indicate that LOX binds to mature TGF-beta1 and enzymatically regulates its signaling in bone and thus may play an important role in bone maintenance and remodeling.
Figures


References
-
- Kagan, H. M., and Li, W. (2003) J. Cell Biochem. 88 660-672 - PubMed
-
- Yeager, V. L., Buranarugsa, M. W., and Arunatut, O. (1985) J. Exp. Pathol. 2 1-11 - PubMed
-
- Ekholm, E. C., Ravanti, L., Kahari, V., Paavolainen, P., and Penttinen, R. P. (2000) Bone (Elmsford) 27 551-557 - PubMed
-
- Li, W., Nugent, M. A., Zhao, Y., Chau, A. N., Li, S. J., Chou, I. N., Liu, G., and Kagan, H. M. (2003) J. Cell Biochem. 88 152-164 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

