Social disparities in BMI trajectories across adulthood by gender, race/ethnicity and lifetime socio-economic position: 1986-2004
- PMID: 18835869
- PMCID: PMC2663716
- DOI: 10.1093/ije/dyn214
Social disparities in BMI trajectories across adulthood by gender, race/ethnicity and lifetime socio-economic position: 1986-2004
Abstract
Background: The prevalence of obesity and overweight is rapidly increasing in industrialized countries, with long-term health and social consequences. There is also a strong social patterning of obesity and overweight, with a higher prevalence among women, racial/ethnic minorities and those from a lower socio-economic position (SEP). Most of the existing work in this area, however, is based on cross-sectional data or single cohort studies. No national studies to date have examined how social disparities in obesity and overweight differ by age and historical period using longitudinal data with repeated measures.
Methods: We used panel data from the nationally representative Monitoring the Future Study (1986-2004) to examine social disparities in trajectories of body mass index (BMI) over adulthood (age 18-45). Self-reported height and weight were collected in this annual US survey of high-school seniors, followed biennially since 1976. Using growth curve models, we analysed BMI trajectories over adulthood by gender, race/ethnicity and lifetime SEP (measured by parents' education and respondent's education).
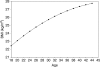
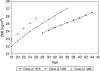
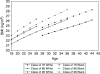
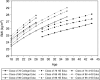
Results: BMI trajectories exhibit a curvilinear rate of change from age 18 to 45, but there was a strong period effect, such that weight gain was more rapid for more recent cohorts. As a result, successive cohorts become overweight (BMI>25) at increasingly earlier points in the life course. BMI scores were also consistently higher for women, racial/ethnic minority groups and those from a lower SEP. However, BMI scores for socially advantaged groups in recent cohorts were actually higher than those for their socially disadvantaged counterparts who were born 10 years earlier.
Conclusions: Results highlight the importance of social status and socio-economic resources for maintaining optimal weight. Yet, even those in advantaged social positions have experienced an increase in BMI in recent years.
Figures
Comment in
-
Commentary: Closing the disparity gaps in obesity.Int J Epidemiol. 2009 Apr;38(2):509-11. doi: 10.1093/ije/dyn352. Int J Epidemiol. 2009. PMID: 19339260 No abstract available.
References
-
- Flegal KM, Carroll MD, Kuczmarski RJ, Johson CL. Overweight and obesity in the United States: prevalence and trends, 1960–1994. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord. 1998;22:39–47. - PubMed
-
- Hedley AA, Ogden CL, Johnson CL, Carroll MD, Curtin LER, Flegal KM. Prevalence of overweight and obesity among US children, adolescents, and adults, 1999–2002. JAMA. 2004;291:2847–50. - PubMed
-
- Lewis CE, Jacobs DR, McCreath H, et al. Weight gain continues in the 1990s: 10 year trends in weight and overweight from the CARDIA study. Am J Epidemiol. 2000;151:1172–81. - PubMed
-
- Mokdad AH, Bowman BA, Ford ES, Vinicor F, Marks JS, Koplan JP. The continuing epidemics of obesity and diabetes in the United States. JAMA. 2001;286:1195–200. - PubMed
-
- Maillard G, Charles MA, Thibult N, et al. Trends in the prevalence of obesity in the French adult population between 1980 and 1991. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord. 1999;23:389–94. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

