Obesity-related upregulation of monocyte chemotactic factors in adipocytes: involvement of nuclear factor-kappaB and c-Jun NH2-terminal kinase pathways
- PMID: 18835938
- PMCID: PMC2606857
- DOI: 10.2337/db07-1344
Obesity-related upregulation of monocyte chemotactic factors in adipocytes: involvement of nuclear factor-kappaB and c-Jun NH2-terminal kinase pathways
Abstract
Objective: We sought to evaluate the entire picture of all monocyte chemotactic factors that potentially contribute to adipose tissue macrophage accumulation in obesity.
Research design and methods: Expression and regulation of members in the entire chemokine superfamily were evaluated in adipose tissue and isolated adipocytes of obese versus lean mice. Kinetics of adipose tissue macrophage infiltration was characterized by fluorescence-activated cell sorting. The effects of fatty acids on stimulation of chemokine expression in adipocytes and underlying mechanisms were investigated.
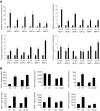
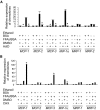
Results: Six monocyte chemotactic factors were found to be predominantly upregulated in isolated adipocytes versus stromal vascular cells in obese mice for the first time, although most of them were previously reported to be upregulated in whole adipose tissue. In diet-induced obese mice, adipose tissue enlargement, increase of adipocyte number, and elevation of multiple chemokine expression precede the initiation of macrophage infiltration. Free fatty acids (FFAs) are found to be inducers for upregulating these chemokines in 3T3-L1 adipocytes, and this effect can be partially blunted by reducing Toll-like receptor 4 expression. FFAs induce expression of monocyte chemotactic factors in adipocytes via both transcription-dependent and -independent mechanisms. In contrast to the reported role of JNK as the exclusive mediator of FFA-induced monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 (MCP-1) expression in macrophages, we show a novel role of inhibitor of kappaB kinase-beta (IKKbeta) in mediating FFA-induced upregulation of all six chemokines and a role of JNK in FFA-induced upregulation of MCP-1 and MCP-3.
Conclusions: Multiple chemokines derived from adipocytes might contribute to obesity-related WAT macrophage infiltration with FFAs as potential triggers and involvement of both IKKbeta and JNK pathways.
Figures



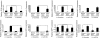


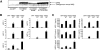
References
-
- Festa A, D'Agostino R Jr, Howard G, Mykkanen L, Tracy RP, Haffner SM: Chronic subclinical inflammation as part of the insulin resistance syndrome: the Insulin Resistance Atherosclerosis Study (IRAS). Circulation 102: 42–47, 2000 - PubMed
-
- Pickup JC, Mattock MB, Chusney GD, Burt D: NIDDM as a disease of the innate immune system: association of acute-phase reactants and interleukin-6 with metabolic syndrome X. Diabetologia 40: 1286–1292, 1997 - PubMed
-
- Ghanim H, Aljada A, Hofmeyer D, Syed T, Mohanty P, Dandona P: Circulating mononuclear cells in the obese are in a proinflammatory state. Circulation 110: 1564–1571, 2004 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

