Chromosomal phylogeny and karyotype evolution in x=7 crucifer species (Brassicaceae)
- PMID: 18836039
- PMCID: PMC2590746
- DOI: 10.1105/tpc.108.062166
Chromosomal phylogeny and karyotype evolution in x=7 crucifer species (Brassicaceae)
Abstract
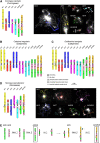
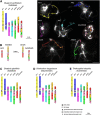
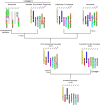
Karyotype evolution in species with identical chromosome number but belonging to distinct phylogenetic clades is a long-standing question of plant biology, intractable by conventional cytogenetic techniques. Here, we apply comparative chromosome painting (CCP) to reconstruct karyotype evolution in eight species with x=7 (2n=14, 28) chromosomes from six Brassicaceae tribes. CCP data allowed us to reconstruct an ancestral Proto-Calepineae Karyotype (PCK; n=7) shared by all x=7 species analyzed. The PCK has been preserved in the tribes Calepineae, Conringieae, and Noccaeeae, whereas karyotypes of Eutremeae, Isatideae, and Sisymbrieae are characterized by an additional translocation. The inferred chromosomal phylogeny provided compelling evidence for a monophyletic origin of the x=7 tribes. Moreover, chromosomal data along with previously published gene phylogenies strongly suggest the PCK to represent an ancestral karyotype of the tribe Brassiceae prior to its tribe-specific whole-genome triplication. As the PCK shares five chromosomes and conserved associations of genomic blocks with the putative Ancestral Crucifer Karyotype (n=8) of crucifer Lineage I, we propose that both karyotypes descended from a common ancestor. A tentative origin of the PCK via chromosome number reduction from n=8 to n=7 is outlined. Comparative chromosome maps of two important model species, Noccaea caerulescens and Thellungiella halophila, and complete karyotypes of two purported autotetraploid Calepineae species (2n=4x=28) were reconstructed by CCP.
Figures

References
-
- Ali, H.B.M., Lysak, M.A., and Schubert, I. (2005). Chromosomal localization of rDNA in the Brassicaceae. Genome 48 341–346. - PubMed
-
- Al-Shehbaz, I.A., Beilstein, M.A., and Kellogg, E.A. (2006). Systematics and phylogeny of the Brassicaceae (Cruciferae): An overview. Plant Syst. Evol. 259 89–120.
-
- Bailey, C.D., Koch, M.A., Mayer, M., Mummenhoff, K., O'Kane, S.L., Jr., Warwick, S.I., Windham, M.D., and Al-Shehbaz, I.A. (2006). Toward a global phylogeny of the Brassicaceae. Mol. Biol. Evol. 23 2142–2160. - PubMed
-
- Beilstein, M.A., Al-Shehbaz, I.A., and Kellogg, E.A. (2006). Brassicaceae phylogeny and trichome evolution. Am. J. Bot. 93 607–619. - PubMed
-
- Berr, A., Pecinka, A., Meister, A., Kreth, G., Fuchs, J., Blattner, F.R., Lysak, M.A., and Schubert, I. (2006). Chromosome arrangement and nuclear architecture but not centromeric sequences are conserved between Arabidopsis thaliana and Arabidopsis lyrata. Plant J. 48 771–783. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

