Gla-rich protein (GRP), a new vitamin K-dependent protein identified from sturgeon cartilage and highly conserved in vertebrates
- PMID: 18836183
- PMCID: PMC2605998
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M802761200
Gla-rich protein (GRP), a new vitamin K-dependent protein identified from sturgeon cartilage and highly conserved in vertebrates
Abstract
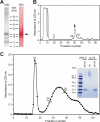
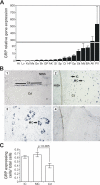
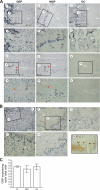
We report the isolation of a novel vitamin K-dependent protein from the calcified cartilage of Adriatic sturgeon (Acipenser nacarii). This 10.2-kDa secreted protein contains 16 gamma-carboxyglutamic acid (Gla) residues in its 74-residue sequence, the highest Gla percent of any known protein, and we have therefore termed it Gla-rich protein (GRP). GRP has a high charge density (36 negative+16 positive=20 net negative) yet is insoluble at neutral pH. GRP has orthologs in all taxonomic groups of vertebrates, and a paralog (GRP2) in bony fish; no GRP homolog was found in invertebrates. There is no significant sequence homology between GRP and the Gla-containing region of any presently known vitamin K-dependent protein. Forty-seven GRP sequences were obtained by a combination of cDNA cloning and comparative genomics: all 47 have a propeptide that contains a gamma-carboxylase recognition site and a mature protein with 14 highly conserved Glu residues, each of them being gamma-carboxylated in sturgeon. The protein sequence of GRP is also highly conserved, with 78% identity between sturgeon and human GRP. Analysis of the corresponding gene structures suggests a highly constrained organization, particularly for exon 4, which encodes the core Gla domain. GRP mRNA is found in virtually all rat and sturgeon tissues examined, with the highest expression in cartilage. Cells expressing GRP include chondrocytes, chondroblasts, osteoblasts, and osteocytes. Because of its potential to bind calcium through Gla residues, we suggest that GRP may regulate calcium in the extracellular environment.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Purification of matrix Gla protein from a marine teleost fish, Argyrosomus regius: calcified cartilage and not bone as the primary site of MGP accumulation in fish.J Bone Miner Res. 2003 Feb;18(2):244-59. doi: 10.1359/jbmr.2003.18.2.244. J Bone Miner Res. 2003. PMID: 12568402
-
Isolation and sequence of the vitamin K-dependent matrix Gla protein from the calcified cartilage of the soupfin shark.J Bone Miner Res. 1994 Apr;9(4):567-76. doi: 10.1002/jbmr.5650090417. J Bone Miner Res. 1994. PMID: 8030445
-
Insights into the association of Gla-rich protein and osteoarthritis, novel splice variants and γ-carboxylation status.Mol Nutr Food Res. 2014 Aug;58(8):1636-46. doi: 10.1002/mnfr.201300941. Epub 2014 May 28. Mol Nutr Food Res. 2014. PMID: 24867294
-
Gla-rich protein, a new player in tissue calcification?Adv Nutr. 2012 Mar 1;3(2):174-81. doi: 10.3945/an.111.001685. Adv Nutr. 2012. PMID: 22516725 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Implication of a novel vitamin K dependent protein, GRP/Ucma in the pathophysiological conditions associated with vascular and soft tissue calcification, osteoarthritis, inflammation, and carcinoma.Int J Biol Macromol. 2018 Jul 1;113:309-316. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2018.02.150. Epub 2018 Feb 27. Int J Biol Macromol. 2018. PMID: 29499263 Review.
Cited by
-
Vitamin K‑dependent proteins involved in bone and cardiovascular health (Review).Mol Med Rep. 2018 Jul;18(1):3-15. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2018.8940. Epub 2018 Apr 27. Mol Med Rep. 2018. PMID: 29749440 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Generation and Evaluation of Novel Biomaterials Based on Decellularized Sturgeon Cartilage for Use in Tissue Engineering.Biomedicines. 2021 Jul 4;9(7):775. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines9070775. Biomedicines. 2021. PMID: 34356839 Free PMC article.
-
The role of vitamin K in soft-tissue calcification.Adv Nutr. 2012 Mar 1;3(2):166-73. doi: 10.3945/an.111.001628. Adv Nutr. 2012. PMID: 22516724 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sturgeon osteocalcin shares structural features with matrix Gla protein: evolutionary relationship and functional implications.J Biol Chem. 2013 Sep 27;288(39):27801-11. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.450213. Epub 2013 Jul 24. J Biol Chem. 2013. PMID: 23884418 Free PMC article.
-
Mycobacterium chelonae associated with tumor-like skin and oral masses in farmed Russian sturgeons (Acipenser gueldenstaedtii).BMC Vet Res. 2014 Jan 14;10:18. doi: 10.1186/1746-6148-10-18. BMC Vet Res. 2014. PMID: 24423126 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

