High sensitivity: high-resolution SPECT-CT/MR molecular imaging of angiogenesis in the Vx2 model
- PMID: 18836386
- PMCID: PMC2703786
- DOI: 10.1097/RLI.0b013e31818935eb
High sensitivity: high-resolution SPECT-CT/MR molecular imaging of angiogenesis in the Vx2 model
Abstract
Objectives: The use of antiangiogenic therapy in conjunction with traditional chemotherapy is becoming increasingly in cancer management, but the optimal benefit of these targeted pharmaceuticals has been limited to a subset of the population treated. Improved imaging probes that permit sensitive detection and high-resolution characterization of tumor angiogenesis could improve patient risk-benefit stratification. The overarching objective of these experiments was to develop a dual modality alpha(nu)beta3-targeted nanoparticle molecular imaging agent that affords sensitive nuclear detection in conjunction with high-resolution MR characterization of tumor angiogenesis.
Materials and methods: In part 1, New Zealand white rabbits (n = 21) bearing 14d Vx2 tumor received either alpha(nu)beta3-targeted 99mTc nanoparticles at doses of 11, 22, or 44 MBq/kg, nontargeted 99mTc nanoparticles at 22 MBq/kg, or alpha(nu)beta3-targeted 99mTc nanoparticles (22 MBq/kg) competitively inhibited with unlabeled alpha(nu)beta3-nanoparticles. All animals were imaged dynamically over 2 hours with a planar camera using a pinhole collimator. In part 2, the effectiveness of alpha(nu)beta3-targeted 99mTc nanoparticles in the Vx2 rabbit model was demonstrated using clinical SPECT-CT imaging techniques. Next, MR functionality was incorporated into alpha(nu)beta3-targeted 99mTc nanoparticles by inclusion of lipophilic gadolinium chelates into the outer phospholipid layer, and the concept of high sensitivity - high-resolution detection and characterization of tumor angiogenesis was shown using sequential SPECT-CT and MR molecular imaging with 3D neovascular mapping.
Results: alpha(nu)beta3-Targeted 99mTc nanoparticles at 22 MBq/kg produced the highest tumor-to-muscle contrast ratio (8.56 +/- 0.13, TMR) versus the 11 MBq/kg (7.32 +/- 0.12) and 44 MBq/kg (6.55 +/- 0.07) doses, (P < 0.05). TMR of nontargeted particles at 22.2 MBq/kg (5.48 +/- 0.09) was less (P < 0.05) than the equivalent dosage of alpha(nu)beta3-targeted 99mTc nanoparticles. Competitively inhibition of 99mTc alpha(nu)beta3-integrin-targeted nanoparticles at 22.2 MBq/kg reduced (P < 0.05) TMR (5.31 +/- 0.06) to the nontargeted control contrast level. Multislice CT imaging could not distinguish the presence of Vx2 tumor implanted in the popliteal fossa from lymph nodes in the same fossa or in the contralateral leg. However, the use of 99mTc alpha(nu)beta3-nanoparticles with SPECT-CT produced a clear neovasculature signal from the tumor that was absent in the nonimplanted hind leg. Using alpha(nu)beta3-targeted 99mTc-gadolinium nanoparticles, the sensitive detection of the Vx2 tumor was extended to allow MR molecular imaging and 3D mapping of angiogenesis in the small tumor, revealing an asymmetrically distributed, patchy neovasculature along the periphery of the cancer.
Conclusion: Dual modality molecular imaging with alpha(nu)beta3-targeted 99mTc-gadolinium nanoparticles can afford highly sensitive and specific localization of tumor angiogenesis, which can be further characterized with high-resolution MR neovascular mapping, which may predict responsiveness to antiangiogenic therapy.
Figures

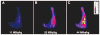




References
-
- Mulder WJ, van der Schaft DW, Hautvast PA, et al. Early in vivo assessment of angiostatic therapy efficacy by molecular MRI. FASEB J. 2007;21:378–383. - PubMed
-
- Sipkins DA, Cheresh DA, Kazemi MR, et al. Detection of tumor angiogenesis in vivo by alpha v beta 3-targeted magnetic resonance imaging. Nat Med. 1998;4:623–626. - PubMed
-
- Winter PM, Caruthers SD, Kassner A, et al. Molecular imaging of angiogenesis in nascent Vx-2 rabbit tumors using a novel alpha(nu-)beta3-targeted nanoparticle and 1.5 tesla magnetic resonance imaging. Cancer Res. 2003;63:5838–5843. - PubMed
-
- Schmieder AH, Winter PM, Caruthers SD, et al. Molecular MR imaging of melanoma angiogenesis with alpha nu beta 3-targeted paramagnetic nanoparticles. Magn Reson Med. 2005;53:621–627. - PubMed
-
- Folkman J. Role of angiogenesis in tumor growth and metastasis. Semin Oncol. 2002;29(suppl 16):15–18. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

