Brain lithium, N-acetyl aspartate and myo-inositol levels in older adults with bipolar disorder treated with lithium: a lithium-7 and proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy study
- PMID: 18837863
- PMCID: PMC4100250
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1399-5618.2008.00627.x
Brain lithium, N-acetyl aspartate and myo-inositol levels in older adults with bipolar disorder treated with lithium: a lithium-7 and proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy study
Abstract
Objectives: We investigated the relationship between brain lithium levels and the metabolites N-acetyl aspartate (NAA) and myo-inositol (myo-Ino) in the anterior cingulate cortex of a group of older adults with bipolar disorder (BD).
Methods: This cross-sectional assessment included nine subjects (six males and three females) with bipolar I disorder and currently treated with lithium, who were examined at McLean Hospital's Geriatric Psychiatry Research Program and Brain Imaging Center. The subjects' ages ranged from 56 to 85 years (66.0 +/- 9.7 years) and all subjects had measurements of serum and brain lithium levels. Brain lithium levels were assessed using lithium magnetic resonance spectroscopy. All subjects also had proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy to obtain measurements of NAA and myo-Ino.
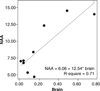
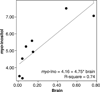
Results: Brain lithium levels were associated with higher NAA levels [df = (1, 8), Beta = 12.53, t = 4.09, p < 0.005] and higher myo-Ino levels [df = (1, 7), F = 16.81, p < 0.006]. There were no significant effects of serum lithium levels on any of the metabolites.
Conclusion: Our findings of a relationship between higher brain lithium levels and elevated NAA levels in older adult subjects with BD may support previous evidence of lithium's neuroprotective, neurotrophic, and mitochondrial function-enhancing effects. Elevated myo-Ino related to elevated brain lithium levels may reflect increased inositol monophosphatase (IMPase) activity, which would lead to an increase in myo-Ino levels. This is the first study to demonstrate alterations in NAA and myo-Ino in a sample of older adults with BD treated with lithium.
Conflict of interest statement
CTF, YAB, MW, and CMM have no reported conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Nambudiri DE, Meyers BS, Young RC. Delayed recovery from lithium neurotoxicity. J Geriatr Psychiatry Neurol. 1991;4:40–43. - PubMed
-
- Bertolino A, Frye M, Callicott JH, et al. Neuronal pathology in the hippocampal area of patients with bipolar disorder: a study with proton magnetic resonance spectroscopic imaging. Biol Psychiatry. 2003;53:906–913. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous