Advances in pemphigus and its endemic pemphigus foliaceus (Fogo Selvagem) phenotype: a paradigm of human autoimmunity
- PMID: 18838249
- PMCID: PMC2704386
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jaut.2008.08.003
Advances in pemphigus and its endemic pemphigus foliaceus (Fogo Selvagem) phenotype: a paradigm of human autoimmunity
Abstract
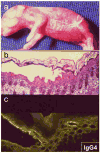
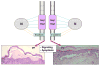
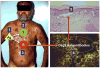
Pemphigus encompasses a group of organ specific, antibody mediated autoimmune diseases of the skin characterized by keratinocyte detachment that leads to the development of blisters and erosions, which can become life-threatening. The pathogenic autoantibodies recognize desmogleins, which are members of the desmosomal cadherin family of cell adhesion molecules. Desmoglein 3 is targeted in pemphigus vulgaris while desmoglein 1 is targeted in pemphigus foliaceus and its endemic form, Fogo Selvagem. This review will briefly define the salient features of pemphigus and the proposed steps in pathogenesis. We will then summarize the most recent advances in three important areas of investigation: (i) epidemiologic, genetic, and immunologic features of Fogo Selvagem, (ii) molecular mechanisms of injury to the epidermis, and (iii) novel therapeutic strategies targeting specific steps in disease pathogenesis. The advances in each of these three seemingly separate areas contribute to the overall understanding of the pemphigus disease model. These recent advancements also underscore the dynamic interplay between the treatment of patients in a clinical setting and basic science research and have led to an integrative understanding of disease pathogenesis and treatment, allowing pemphigus to serve as a paradigm of human autoimmunity.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors state no conflict of interest.
Figures


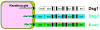
References
-
- Anhalt GJ, Labib RS, Voorhees JJ, Beals TF, Diaz LA. Induction of pemphigus in neonatal mice by passive transfer of IgG from patients with the disease. N Engl J Med. 1982;306:1189–1196. - PubMed
-
- Roscoe JT, Diaz L, Sampaio SA, Castro RM, Labib RS, Takahashi Y, Patel H, Anhalt GJ. Brazilian pemphigus foliaceus autoantibodies are pathogenic to BALB/c mice by passive transfer. J Invest Dermatol. 1985;85:538–541. - PubMed
-
- Udey MC, Stanley JR. Pemphigus--diseases of antidesmosomal autoimmunity. Jama. 1999;282:572–576. - PubMed
-
- Emery DJ, Diaz LA, Fairley JA, Lopez A, Taylor AF, Giudice GJ. Pemphigus foliaceus and pemphigus vulgaris autoantibodies react with the extracellular domain of desmoglein-1. J Invest Dermatol. 1995;104:323–328. - PubMed
-
- Futamura S, Martins C, Rivitti EA, Labib RS, Diaz LA, Anhalt GJ. Ultrastructural studies of acantholysis induced in vivo by passive transfer of IgG from endemic pemphigus foliaceus (Fogo Selvagem) J Invest Dermatol. 1989;93:480–485. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

