Assembly of erodible, DNA-containing thin films on the surfaces of polymer microparticles: toward a layer-by-layer approach to the delivery of DNA to antigen-presenting cells
- PMID: 18838346
- PMCID: PMC2667125
- DOI: 10.1016/j.actbio.2008.08.022
Assembly of erodible, DNA-containing thin films on the surfaces of polymer microparticles: toward a layer-by-layer approach to the delivery of DNA to antigen-presenting cells
Abstract
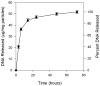
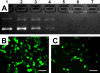
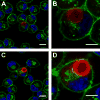
We report a layer-by-layer approach to the assembly of ultrathin and erodible DNA-containing films on the surfaces of polymer microparticles. DNA-containing multilayered films were fabricated layer-by-layer on the surfaces of polystyrene microspheres (approximately 6 microm) by iterative and alternating cycles of particle suspension, centrifugation and resuspension in solutions of plasmid DNA and a hydrolytically degradable polyamine. Film growth occurred in a stepwise manner, as demonstrated by characterization of the zeta potentials and fluorescence intensities of film-coated particles during film assembly. Characterization of film-coated particles by confocal fluorescence microscopy and scanning electron microscopy revealed the multilayered particle coatings to be smooth, uniform and free of large-scale physical defects. Film-coated microparticles sustained the release of transcriptionally active DNA into solution for approximately three days when incubated in physiologically relevant media. Previous studies have demonstrated that the adsorption of DNA onto the surfaces of cationic microparticles can be used to target the delivery of DNA to antigen-presenting cells. As a first step toward the application of this layer-by-layer approach to the development of methods for the delivery of DNA to antigen-presenting cells, we demonstrated that film-coated microparticles could be used to transport DNA into macrophage cells in vitro using a model mouse macrophage cell line. Our results suggest the basis of a general approach that could, with further development, prove useful for the delivery of DNA-encoded antigens to macrophages, or other antigen-presenting cells, and provide new materials-based methods for the formulation and delivery of DNA vaccines.
Figures

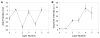
Similar articles
-
Rapid release of plasmid DNA from surfaces coated with polyelectrolyte multilayers promoted by the application of electrochemical potentials.ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2012 May;4(5):2726-34. doi: 10.1021/am3003632. Epub 2012 May 3. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2012. PMID: 22551230 Free PMC article.
-
Release of plasmid DNA from intravascular stents coated with ultrathin multilayered polyelectrolyte films.Biomacromolecules. 2006 Sep;7(9):2483-91. doi: 10.1021/bm0604808. Biomacromolecules. 2006. PMID: 16961308 Free PMC article.
-
DNA delivery in vitro via surface release from multilayer assemblies with poly(glycoamidoamine)s.Acta Biomater. 2009 Mar;5(3):925-33. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2009.01.001. Epub 2009 Jan 13. Acta Biomater. 2009. PMID: 19249723
-
Multilayered polyelectrolyte assemblies as platforms for the delivery of DNA and other nucleic acid-based therapeutics.Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2008 Jun 10;60(9):979-99. doi: 10.1016/j.addr.2008.02.010. Epub 2008 Mar 4. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2008. PMID: 18395291 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Biomedical applications of electrostatic layer-by-layer nano-assembly of polymers, enzymes, and nanoparticles.Cell Biochem Biophys. 2003;39(1):23-43. doi: 10.1385/CBB:39:1:23. Cell Biochem Biophys. 2003. PMID: 12835527 Review.
Cited by
-
Degradable polyelectrolyte multilayers that promote the release of siRNA.Langmuir. 2011 Jun 21;27(12):7868-76. doi: 10.1021/la200815t. Epub 2011 May 16. Langmuir. 2011. PMID: 21574582 Free PMC article.
-
Reduction of intimal hyperplasia in injured rat arteries promoted by catheter balloons coated with polyelectrolyte multilayers that contain plasmid DNA encoding PKCδ.Biomaterials. 2013 Jan;34(1):226-36. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2012.09.010. Epub 2012 Oct 13. Biomaterials. 2013. PMID: 23069712 Free PMC article.
-
Rapid release of plasmid DNA from surfaces coated with polyelectrolyte multilayers promoted by the application of electrochemical potentials.ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2012 May;4(5):2726-34. doi: 10.1021/am3003632. Epub 2012 May 3. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2012. PMID: 22551230 Free PMC article.
-
A pH-sensitive multifunctional gene carrier assembled via layer-by-layer technique for efficient gene delivery.Int J Nanomedicine. 2012;7:925-39. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S26955. Epub 2012 Feb 21. Int J Nanomedicine. 2012. PMID: 22393290 Free PMC article.
-
Electrical characterization of DNA supported on nitrocellulose membranes.Sci Rep. 2016 Jul 12;6:29089. doi: 10.1038/srep29089. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27404401 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

