AKT alters genome-wide estrogen receptor alpha binding and impacts estrogen signaling in breast cancer
- PMID: 18838536
- PMCID: PMC2593438
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.00799-08
AKT alters genome-wide estrogen receptor alpha binding and impacts estrogen signaling in breast cancer
Abstract
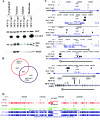
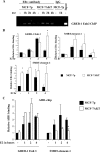
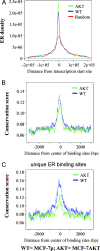
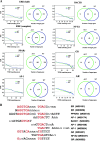
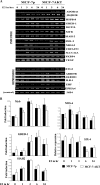
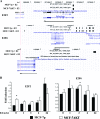
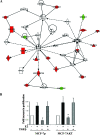
Estrogen regulates several biological processes through estrogen receptor alpha (ERalpha) and ERbeta. ERalpha-estrogen signaling is additionally controlled by extracellular signal activated kinases such as AKT. In this study, we analyzed the effect of AKT on genome-wide ERalpha binding in MCF-7 breast cancer cells. Parental and AKT-overexpressing cells displayed 4,349 and 4,359 ERalpha binding sites, respectively, with approximately 60% overlap. In both cell types, approximately 40% of estrogen-regulated genes associate with ERalpha binding sites; a similar percentage of estrogen-regulated genes are differentially expressed in two cell types. Based on pathway analysis, these differentially estrogen-regulated genes are linked to transforming growth factor beta (TGF-beta), NF-kappaB, and E2F pathways. Consistent with this, the two cell types responded differently to TGF-beta treatment: parental cells, but not AKT-overexpressing cells, required estrogen to overcome growth inhibition. Combining the ERalpha DNA-binding pattern with gene expression data from primary tumors revealed specific effects of AKT on ERalpha binding and estrogen-regulated expression of genes that define prognostic subgroups and tamoxifen sensitivity of ERalpha-positive breast cancer. These results suggest a unique role of AKT in modulating estrogen signaling in ERalpha-positive breast cancers and highlights how extracellular signal activated kinases can change the landscape of transcription factor binding to the genome.
Figures
References
-
- Ali, S., and R. C. Coombes. 2002. Endocrine-responsive breast cancer and strategies for combating resistance. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2101-112. - PubMed
-
- Anzick, S. L., J. Kononen, R. L. Walker, D. O. Azorsa, M. M. Tanner, X. Y. Guan, G. Sauter, O. P. Kallioniemi, J. M. Trent, and P. S. Meltzer. 1997. AIB1, a steroid receptor coactivator amplified in breast and ovarian cancer. Science 277965-968. - PubMed
-
- Auboeuf, D., A. Honig, S. M. Berget, and B. W. O'Malley. 2002. Coordinate regulation of transcription and splicing by steroid receptor coregulators. Science 298416-419. - PubMed
-
- Bellacosa, A., D. de Feo, A. K. Godwin, D. W. Bell, J. Q. Cheng, D. A. Altomare, M. Wan, L. Dubeau, G. Scambia, V. Masciullo, et al. 1995. Molecular alterations of the AKT2 oncogene in ovarian and breast carcinomas. Int. J. Cancer 64280-285. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
