The keratin-binding protein Albatross regulates polarization of epithelial cells
- PMID: 18838552
- PMCID: PMC2557036
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.200803133
The keratin-binding protein Albatross regulates polarization of epithelial cells
Abstract
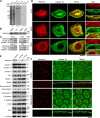
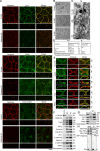
The keratin intermediate filament network is abundant in epithelial cells, but its function in the establishment and maintenance of cell polarity is unclear. Here, we show that Albatross complexes with Par3 to regulate formation of the apical junctional complex (AJC) and maintain lateral membrane identity. In nonpolarized epithelial cells, Albatross localizes with keratin filaments, whereas in polarized epithelial cells, Albatross is primarily localized in the vicinity of the AJC. Knockdown of Albatross in polarized cells causes a disappearance of key components of the AJC at cell-cell borders and keratin filament reorganization. Lateral proteins E-cadherin and desmoglein 2 were mislocalized even on the apical side. Although Albatross promotes localization of Par3 to the AJC, Par3 and ezrin are still retained at the apical surface in Albatross knockdown cells, which retain intact microvilli. Analysis of keratin-deficient epithelial cells revealed that keratins are required to stabilize the Albatross protein, thus promoting the formation of AJC. We propose that keratins and the keratin-binding protein Albatross are important for epithelial cell polarization.
Figures



References
-
- Bornslaeger, E.A., C.M. Corcoran, T.S. Stappenbeck, and K.J. Green. 1996. Breaking the connection: displacement of the desmosomal plaque protein desmoplakin from cell-cell interfaces disrupts anchorage of intermediate filament bundles and alters intercellular junction assembly. J. Cell Biol. 134:985–1001. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Chen, X., and I.G. Macara. 2005. Par-3 controls tight junction assembly through the Rac exchange factor Tiam1. Nat. Cell Biol. 7:262–269. - PubMed
-
- Coulombe, P.A., and P. Wong. 2004. Cytoplasmic intermediate filaments revealed as dynamic and multipurpose scaffolds. Nat. Cell Biol. 6:699–706. - PubMed
-
- Fuchs, E., and D.W. Cleveland. 1998. A structural scaffolding of intermediate filaments in health and disease. Science. 279:514–519. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

