Dephosphorylation by calcineurin regulates translocation of Drp1 to mitochondria
- PMID: 18838687
- PMCID: PMC2572940
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0808249105
Dephosphorylation by calcineurin regulates translocation of Drp1 to mitochondria
Abstract
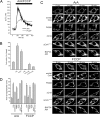
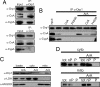
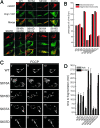
Changes in mitochondrial morphology that occur during cell cycle, differentiation, and death are tightly regulated by the balance between fusion and fission processes. Excessive fragmentation can be caused by inhibition of the fusion machinery and is a common consequence of dysfunction of the organelle. Here, we show a role for calcineurin-dependent translocation of the profission dynamin related protein 1 (Drp1) to mitochondria in dysfunction-induced fragmentation. When mitochondrial depolarization is associated with sustained cytosolic Ca(2+) rise, it activates the cytosolic phosphatase calcineurin that normally interacts with Drp1. Calcineurin-dependent dephosphorylation of Drp1, and in particular of its conserved serine 637, regulates its translocation to mitochondria as substantiated by site directed mutagenesis. Thus, fragmentation of depolarized mitochondria depends on a loop involving sustained Ca(2+) rise, activation of calcineurin, and dephosphorylation of Drp1 and its translocation to the organelle.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Meeusen SL, Nunnari J. How mitochondria fuse. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2005;17:389–394. - PubMed
-
- McBride HM, Neuspiel M, Wasiak S. Mitochondria: More than just a powerhouse. Curr Biol. 2006;16:R551–R560. - PubMed
-
- Pellegrini L, Scorrano L. A cut short to death: Parl and Opa1 in the regulation of mitochondrial morphology and apoptosis. Cell Death Differ. 2007;14:1275–1284. - PubMed
-
- Okamoto K, Shaw JM. Mitochondrial morphology and dynamics in yeast and multicellular eukaryotes. Annu Rev Genet. 2005;39:503–536. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

