Fast quantitative determination of microbial rhamnolipids from cultivation broths by ATR-FTIR Spectroscopy
- PMID: 18840269
- PMCID: PMC2572035
- DOI: 10.1186/1754-1611-2-13
Fast quantitative determination of microbial rhamnolipids from cultivation broths by ATR-FTIR Spectroscopy
Abstract
Background: Vibrational spectroscopic techniques are becoming increasingly important and popular because they have the potential to provide rapid and convenient solutions to routine analytical problems. Using these techniques, a variety of substances can be characterized, identified and also quantified rapidly.
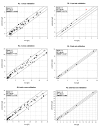
Results: The rapid ATR-FTIR (Attenuated Total Reflectance Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy) in time technique has been applied, which is suitable to quantify the concentrations of microbial rhamnolipids in a typical cultivation process. While the usually applied HPLC analysis requires an extensive and time consuming multi step extraction protocol for sample preparation, the ATR-FTIR-method allows the quantification of the rhamnolipids within 20 minutes. Accuracies between 0.5 g/l - 2.1 g/l for the different analytes were determined by cross validation of the calibration set. Even better accuracies between 0.28 g/l - 0.59 g/l were found for independent test samples of an arbitrarily selected cultivation.
Conclusion: ATR-FTIR was found to be suitable for the rapid analysis of rhamnolipids in a biotechnological process with good reproducibility in sample determination and sufficient accuracy. An improvement in accuracy through continuous expansion and validation of the reference spectra set seems very likely.
Figures



References
-
- Antranikian G. Angewandte Mikrobiologie. 1. Berlin, Heidelberg, New York: Springer-Verlag; 2006.
-
- Tanaka T, Nagao S, Ogawa H. Attenuated Total Reflection Fourier Transform Infrared (ATR-FTIR) Spectroscopy of Functional Groups of Humic Acid Dissolving in Aqueous Solution. Anal Sci. 2001;17:i1081–i1084.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

