Quantum dots and nanoparticles for photodynamic and radiation therapies of cancer
- PMID: 18840487
- PMCID: PMC2695009
- DOI: 10.1016/j.addr.2008.08.004
Quantum dots and nanoparticles for photodynamic and radiation therapies of cancer
Abstract
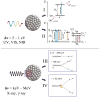
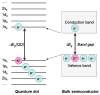
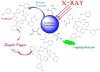
Semiconductor quantum dots and nanoparticles composed of metals, lipids or polymers have emerged with promising applications for early detection and therapy of cancer. Quantum dots with unique optical properties are commonly composed of cadmium contained semiconductors. Cadmium is potentially hazardous, and toxicity of such quantum dots to living cells, and humans, is not yet systematically investigated. Therefore, search for less toxic materials with similar targeting and optical properties is of further interest. Whereas, the investigation of luminescence nanoparticles as light sources for cancer therapy is very interesting. Despite advances in neurosurgery and radiotherapy the prognosis for patients with malignant gliomas has changed little for the last decades. Cancer treatment requires high accuracy in delivering ionizing radiation to reduce toxicity to surrounding tissues. Recently some research has been focused in developing photosensitizing quantum dots for production of radicals upon absorption of visible light. In spite of the fact that visible light is safe, this approach is suitable to treat only superficial tumours. Ionizing radiation (X-rays and gamma rays) penetrate much deeper thus offering a big advantage in treating patients with tumours in internal organs. Such concept of using quantum dots and nanoparticles to yield electrons and radicals in photodynamic and radiation therapies as well their combination is reviewed in this article.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Interaction of porphyrins with CdTe quantum dots.Nanotechnology. 2011 May 13;22(19):195501. doi: 10.1088/0957-4484/22/19/195501. Epub 2011 Mar 23. Nanotechnology. 2011. PMID: 21430318
-
Quantum dots and their potential biomedical applications in photosensitization for photodynamic therapy.Nanomedicine (Lond). 2009 Apr;4(3):353-63. doi: 10.2217/nnm.09.9. Nanomedicine (Lond). 2009. PMID: 19331542 Review.
-
Using nanoparticles to enable simultaneous radiation and photodynamic therapies for cancer treatment.J Nanosci Nanotechnol. 2006 Apr;6(4):1159-66. doi: 10.1166/jnn.2006.327. J Nanosci Nanotechnol. 2006. PMID: 16736782 Review.
-
Luminescent behavior of cadmium sulfide quantum dots for gallic acid estimation.Nanotechnology. 2013 Mar 22;24(11):115602. doi: 10.1088/0957-4484/24/11/115602. Epub 2013 Feb 28. Nanotechnology. 2013. PMID: 23448947
-
Rational engineering of semiconductor QDs enabling remarkable 1O2 production for tumor-targeted photodynamic therapy.Biomaterials. 2017 Dec;148:31-40. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2017.09.026. Epub 2017 Sep 20. Biomaterials. 2017. PMID: 28961533
Cited by
-
Bionanotechnology and the future of glioma.Surg Neurol Int. 2015 Feb 13;6(Suppl 1):S45-58. doi: 10.4103/2152-7806.151334. eCollection 2015. Surg Neurol Int. 2015. PMID: 25722933 Free PMC article.
-
Modern micro and nanoparticle-based imaging techniques.Sensors (Basel). 2012 Nov 2;12(11):14792-820. doi: 10.3390/s121114792. Sensors (Basel). 2012. PMID: 23202187 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Photon activated therapy (PAT) using monochromatic synchrotron X-rays and iron oxide nanoparticles in a mouse tumor model: feasibility study of PAT for the treatment of superficial malignancy.Radiat Oncol. 2012 Oct 31;7:184. doi: 10.1186/1748-717X-7-184. Radiat Oncol. 2012. PMID: 23111059 Free PMC article.
-
Preparation of quantum dot/drug nanoparticle formulations for traceable targeted delivery and therapy.Theranostics. 2012;2(7):681-94. doi: 10.7150/thno.3692. Epub 2012 Jul 27. Theranostics. 2012. PMID: 22896770 Free PMC article.
-
Current Strategies for Tumor Photodynamic Therapy Combined With Immunotherapy.Front Oncol. 2021 Nov 17;11:738323. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.738323. eCollection 2021. Front Oncol. 2021. PMID: 34868932 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Samia AC, Dayal S, Burda C. Quantum dot-based energy transfer: perspectives and potential for applications in photodynamic therapy. Photochem Photobiol. 2006;82:617–625. - PubMed
-
- Chen W. Nanoparticle fluorescence based technology for biological applications. J Nanosci Nanotechnol. 2008;8:1019–1051. - PubMed
-
- Jovin TM. Quantum dots finally come of age. Nat Biotechnol. 2003;21:32–33. - PubMed
-
- Smith AM, Gao X, Nie S. Quantum dot nanocrystals for in vivo molecular and cellular imaging. Photochem Photobiol. 2004;80:377–385. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

