Hepatitis C virus NS5B polymerase exhibits distinct nucleotide requirements for initiation and elongation
- PMID: 18840605
- PMCID: PMC2662215
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M803094200
Hepatitis C virus NS5B polymerase exhibits distinct nucleotide requirements for initiation and elongation
Abstract
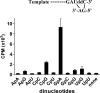
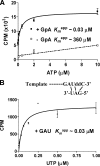
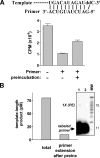
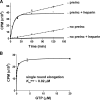
The hepatitis C virus (HCV) NS5B protein is an RNA-dependent RNA polymerase (RdRp) essential for replication of the viral RNA genome. Purified NS5B has been reported to exhibit multiple activities in vitro. Using a synthetic heteropolymeric RNA template with dideoxycytidine at its 3'-end, we examined de novo initiation and primer extension in a system devoid of self-priming and terminal nucleotide transferase activities. Products predominantly of template size and its multiples were detected. High concentrations of nucleoside triphosphates (K(app)(m) approximately 100-400 mum) corresponding to the first three incorporated nucleotides were found to be required for efficient de novo RNA synthesis. In the presence of initiating di- or trinucleotides, however, the amount of NTP needed to achieve maximal activity dropped 10(3)- to 10(4)-fold, revealing a much reduced nucleotide requirement for elongation (K(app)(m) approximately 0.03-0.09 microm). Accordingly, single round extension from an exogenous primer following preincubation of the enzyme with template and primer could also be supported by <0.1 microm levels of NTP. De novo synthesis at high NTP concentrations was shown to be preferred over primer extension. On a dideoxycytidine-blocked synthetic RNA template derived from the 3'-end of the HCV(-)UTR, the addition of the corresponding initiating trinucleotide also dramatically reduced the NTP levels needed to achieve efficient RNA synthesis. Thus, distinct nucleotide requirements exist for initiation and elongation steps catalyzed by the HCV NS5B polymerase.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Enzymatic characterization of the full-length and C-terminally truncated hepatitis C virus RNA polymerases: function of the last 21 amino acids of the C terminus in template binding and RNA synthesis.Biochemistry. 2004 Aug 17;43(32):10579-91. doi: 10.1021/bi049773g. Biochemistry. 2004. PMID: 15301555
-
De novo initiation of RNA synthesis by the RNA-dependent RNA polymerase (NS5B) of hepatitis C virus.J Virol. 2000 Jan;74(2):851-63. doi: 10.1128/jvi.74.2.851-863.2000. J Virol. 2000. PMID: 10623748 Free PMC article.
-
Selection of 3'-template bases and initiating nucleotides by hepatitis C virus NS5B RNA-dependent RNA polymerase.J Virol. 2002 Jul;76(14):7030-9. doi: 10.1128/jvi.76.14.7030-7039.2002. J Virol. 2002. PMID: 12072503 Free PMC article.
-
Biochemical and structural analysis of the NS5B RNA-dependent RNA polymerase of the hepatitis C virus.J Viral Hepat. 2000 May;7(3):167-74. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2893.2000.00218.x. J Viral Hepat. 2000. PMID: 10849258 Review.
-
Nucleoside, nucleotide, and non-nucleoside inhibitors of hepatitis C virus NS5B RNA-dependent RNA-polymerase.J Med Chem. 2012 Mar 22;55(6):2481-531. doi: 10.1021/jm201384j. Epub 2012 Jan 23. J Med Chem. 2012. PMID: 22185586 Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Hepatitis C virus RNA replication and assembly: living on the fat of the land.Cell Host Microbe. 2014 Nov 12;16(5):569-79. doi: 10.1016/j.chom.2014.10.008. Epub 2014 Nov 12. Cell Host Microbe. 2014. PMID: 25525790 Free PMC article. Review.
-
De novo polymerase activity and oligomerization of hepatitis C virus RNA-dependent RNA-polymerases from genotypes 1 to 5.PLoS One. 2011 Apr 7;6(4):e18515. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0018515. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 21490973 Free PMC article.
-
Discovery of new scaffolds for rational design of HCV NS5B polymerase inhibitors.Eur J Med Chem. 2012 Dec;58:258-64. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2012.09.010. Epub 2012 Sep 17. Eur J Med Chem. 2012. PMID: 23127989 Free PMC article.
-
Structural and functional analysis of hepatitis C virus strain JFH1 polymerase.J Virol. 2009 Nov;83(22):11926-39. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01008-09. Epub 2009 Sep 9. J Virol. 2009. PMID: 19740982 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibitors of the Hepatitis C Virus RNA-Dependent RNA Polymerase NS5B.Viruses. 2010 Oct;2(10):2169-2195. doi: 10.3390/v2102169. Epub 2010 Sep 28. Viruses. 2010. PMID: 21994615 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alter, H. J., and Seeff, L. B. (2000) Semin. Liver Dis. 20 17–35 - PubMed
-
- National Institutes of Health (2002) Hepatology 36 S3–S20 - PubMed
-
- Reed, K. E., and Rice, C. M. (2000) in Current Topics in Microbiology and Immunology: The Hepatitis C Viruses (Hagedorn, C. H., and Rice, C. M., eds) Vol. 242, 55–84 Springer, Heidelberg - PubMed
-
- Carroll, S. S., and Olsen, D. B. (2006) Infect. Disord. Drug Targets 6 17–29 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

