Neuronal pentraxins modulate cocaine-induced neuroadaptations
- PMID: 18840757
- PMCID: PMC2610018
- DOI: 10.1124/jpet.108.143115
Neuronal pentraxins modulate cocaine-induced neuroadaptations
Abstract
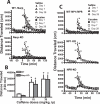
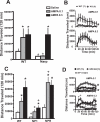
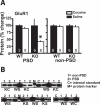
Neuronal pentraxins (NPs) function in the extracellular matrix to bind alpha-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazolepropionic acid (AMPA) receptors. Three NPs have been described, neuronal activity-regulated pentraxin (Narp), which is regulated as an immediate early gene, NP1, and neuronal pentraxin receptor (NPR). Narp and NP1 enhance synaptogenesis and glutamate signaling by clustering AMPA receptors, whereas NPR contributes to removing AMPA receptors during group I metabotropic glutamate receptor-dependent long-term depression. Here, we examine mice with genetic deletions [knockout (KO)] of each NP to assess their contributions to cocaine-induced neuroplasticity. Consistent with a shared AMPA receptor clustering function for Narp and NP1, deletion of either NP caused similar behavioral alterations. Thus, although both Narp and NP1 deletion promoted cocaine-induced place preference, NPR deletion was without effect. In addition, although Narp and NP1 KO showed reduced time in the center of a novel environment, NPR KO mice spent more time in the center. Finally, although Narp and NP1 KO mice showed blunted locomotion after AMPA microinjection into the accumbens 3 weeks after discontinuing repeated cocaine injections, the AMPA response was augmented in NPR KO. Likewise, endogenous glutamate release elicited less motor activity in Narp KO mice. Consistent with reduced AMPA responsiveness after chronic cocaine in Narp KO mice, glutamate receptor 1 was reduced in the PSD fraction of Narp KO mice withdrawn from cocaine. These data indicate that NPs differentially contribute to cocaine-induced plasticity in a manner that parallels their actions in synaptic plasticity.
Figures



Similar articles
-
The Role of AMPAR Trafficking Mediated by Neuronal Pentraxins in Cocaine-induced Neuroadaptations.Mol Cell Pharmacol. 2009 May 6;1(2):183-192. doi: 10.4255/mcpharmacol.09.08. Mol Cell Pharmacol. 2009. PMID: 20336176 Free PMC article.
-
Presynaptic Neuronal Pentraxin Receptor Organizes Excitatory and Inhibitory Synapses.J Neurosci. 2017 Feb 1;37(5):1062-1080. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2768-16.2016. Epub 2016 Dec 16. J Neurosci. 2017. PMID: 27986928 Free PMC article.
-
Ethanol up-regulates nucleus accumbens neuronal activity dependent pentraxin (Narp): implications for alcohol-induced behavioral plasticity.Alcohol. 2012 Jun;46(4):377-87. doi: 10.1016/j.alcohol.2011.10.003. Epub 2012 Mar 22. Alcohol. 2012. PMID: 22444953 Free PMC article.
-
Hypoxic-ischemic injury in neonatal brain: involvement of a novel neuronal molecule in neuronal cell death and potential target for neuroprotection.Int J Dev Neurosci. 2008 Feb;26(1):93-101. doi: 10.1016/j.ijdevneu.2007.08.013. Epub 2007 Sep 7. Int J Dev Neurosci. 2008. PMID: 17936538 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mediating the effects of drug abuse: the role of Narp in synaptic plasticity.ILAR J. 2011;52(3):321-8. doi: 10.1093/ilar.52.3.321. ILAR J. 2011. PMID: 23382146 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Gene-environment interactions mediate stress susceptibility and resilience through the CaMKIIβ/TARPγ-8/AMPAR pathway.iScience. 2021 May 2;24(5):102504. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2021.102504. eCollection 2021 May 21. iScience. 2021. PMID: 34113835 Free PMC article.
-
Npas4 regulates medium spiny neuron physiology and gates cocaine-induced hyperlocomotion.EMBO Rep. 2021 Dec 6;22(12):e51882. doi: 10.15252/embr.202051882. Epub 2021 Oct 18. EMBO Rep. 2021. PMID: 34661342 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of AMPAR Trafficking Mediated by Neuronal Pentraxins in Cocaine-induced Neuroadaptations.Mol Cell Pharmacol. 2009 May 6;1(2):183-192. doi: 10.4255/mcpharmacol.09.08. Mol Cell Pharmacol. 2009. PMID: 20336176 Free PMC article.
-
Adaptor protein APPL1 couples synaptic NMDA receptor with neuronal prosurvival phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt pathway.J Neurosci. 2012 Aug 29;32(35):11919-29. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3852-11.2012. J Neurosci. 2012. PMID: 22933778 Free PMC article.
-
AMPA receptor synaptic plasticity induced by psychostimulants: the past, present, and therapeutic future.Neuron. 2010 Jul 15;67(1):11-24. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2010.06.004. Neuron. 2010. PMID: 20624588 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bachtell RK, Choi KH, Simmons DL, Falcon E, Monteggia LM, Neve RL, Self DW. Role of GluR1 expression in nucleus accumbens neurons in cocaine sensitization and cocaine-seeking behavior. Eur J Neurosci. 2008;27:2229–2240. - PubMed
-
- Bardo MT, Bevins RA. Conditioned place preference: what does it add to our preclinical understanding of drug reward? Psychopharmacology. 2000;153:31–43. - PubMed
-
- Bell K, Kalivas PW. Context-specific cross-sensitization between systemic cocaine and intra-accumbens AMPA infusion in the rat. Psychopharmacology. 1996;127:377–383. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

