Inhibition of dipeptidyl peptidase-4 by vildagliptin during glucagon-like Peptide 1 infusion increases liver glucose uptake in the conscious dog
- PMID: 18840785
- PMCID: PMC2606880
- DOI: 10.2337/db08-0515
Inhibition of dipeptidyl peptidase-4 by vildagliptin during glucagon-like Peptide 1 infusion increases liver glucose uptake in the conscious dog
Abstract
Objective: This study investigated the acute effects of treatment with vildagliptin on dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP-4) activity, glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP-1) concentration, pancreatic hormone levels, and glucose metabolism. The primary aims were to determine the effects of DPP-4 inhibition on GLP-1 clearance and on hepatic glucose uptake.
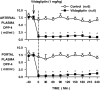
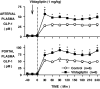
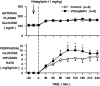
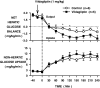
Research design and methods: Fasted conscious dogs were studied in the presence (n = 6) or absence (control, n = 6) of oral vildagliptin (1 mg/kg). In both groups, GLP-1 was infused into the portal vein (1 pmol . kg(-1) . min(-1)) for 240 min. During the same time, glucose was delivered into the portal vein at 4 mg . kg(-1) . min(-1) and into a peripheral vein at a variable rate to maintain the arterial plasma glucose level at 160 mg/dl.
Results: Vildagliptin fully inhibited DPP-4 over the 4-h experimental period. GLP-1 concentrations were increased in the vildagliptin-treated group (50 +/- 3 vs. 85 +/- 7 pmol/l in the portal vein in control and vildagliptin-treated dogs, respectively; P < 0.05) as a result of a 40% decrease in GLP-1 clearance (38 +/- 5 and 22 +/- 2 ml . kg(-1) . min(-1), respectively; P < 0.05). Although hepatic insulin and glucagon levels were not significantly altered, there was a tendency for plasma insulin to be greater (hepatic levels were 73 +/- 10 vs. 88 +/- 15 microU/ml, respectively). During vildagliptin treatment, net hepatic glucose uptake was threefold greater than in the control group. This effect was greater than that predicted by the change in insulin.
Conclusions: Vildagliptin fully inhibited DPP-4 activity, reduced GLP-1 clearance by 40%, and increased hepatic glucose disposal by means beyond the effects of GLP-1 on insulin and glucagon secretion.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Mechanisms of action of the dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitor vildagliptin in humans.Diabetes Obes Metab. 2011 Sep;13(9):775-83. doi: 10.1111/j.1463-1326.2011.01414.x. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2011. PMID: 21507182 Review.
-
Feedback suppression of meal-induced glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) secretion mediated through elevations in intact GLP-1 caused by dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibition: a randomized, prospective comparison of sitagliptin and vildagliptin treatment.Diabetes Obes Metab. 2016 Nov;18(11):1100-1109. doi: 10.1111/dom.12706. Epub 2016 Aug 17. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2016. PMID: 27300579 Clinical Trial.
-
Effects of the dipeptidyl peptidase-IV inhibitor vildagliptin on incretin hormones, islet function, and postprandial glycemia in subjects with impaired glucose tolerance.Diabetes Care. 2008 Jan;31(1):30-5. doi: 10.2337/dc07-1616. Epub 2007 Oct 18. Diabetes Care. 2008. PMID: 17947341 Clinical Trial.
-
Effects of dipeptidyl peptidase IV inhibition on glycemic, gut hormone, triglyceride, energy expenditure, and energy intake responses to fat in healthy males.Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2014 Nov 1;307(9):E830-7. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.00370.2014. Epub 2014 Sep 16. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2014. PMID: 25231186 Clinical Trial.
-
The islet enhancer vildagliptin: mechanisms of improved glucose metabolism.Int J Clin Pract Suppl. 2008 Mar;(159):8-14. doi: 10.1111/j.1742-1241.2007.01685.x. Int J Clin Pract Suppl. 2008. PMID: 18269436 Review.
Cited by
-
Atypical mechanism of glucose modulation by colesevelam in patients with type 2 diabetes.Clin Med Insights Endocrinol Diabetes. 2013 Dec 8;6:75-9. doi: 10.4137/CMED.S12590. Clin Med Insights Endocrinol Diabetes. 2013. PMID: 24348081 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Serum dipeptidyl peptidase-4 activity in insulin resistant patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: a novel liver disease biomarker.PLoS One. 2010 Aug 18;5(8):e12226. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0012226. PLoS One. 2010. PMID: 20805868 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of sitagliptin on ectopic fat contents and glucose metabolism in type 2 diabetic patients with fatty liver: A pilot study.J Diabetes Investig. 2015 Mar;6(2):164-72. doi: 10.1111/jdi.12262. Epub 2014 Aug 6. J Diabetes Investig. 2015. PMID: 25802724 Free PMC article.
-
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and type 2 diabetes mellitus: the liver disease of our age?World J Gastroenterol. 2014 Jul 21;20(27):9072-89. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i27.9072. World J Gastroenterol. 2014. PMID: 25083080 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effects of intraportal exenatide on hepatic glucose metabolism in the conscious dog.Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2013 Jul 1;305(1):E132-9. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.00160.2013. Epub 2013 May 14. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2013. PMID: 23673158 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Drucker DJ: The biology of incretin hormones. Cell Metab 3: 153–165, 2006 - PubMed
-
- Zander M, Madsbad S, Madsen JL, Holst JJ: Effect of 6-week course of glucagon-like peptide 1 on glycaemic control, insulin sensitivity, and beta-cell function in type 2 diabetes: a parallel-group study. Lancet 359: 824–830, 2002 - PubMed
-
- Deacon CF, Nauck MA, Toft-Nielsen M, Pridal L, Willms B, Holst JJ: Both subcutaneously and intravenously administered glucagon-like peptide I are rapidly degraded from the NH2-terminus in type II diabetic patients and in healthy subjects. Diabetes 44: 1126–1131, 1995 - PubMed
-
- Vilsboll T, Agerso H, Krarup T, Holst JJ: Similar elimination rates of glucagon-like peptide-1 in obese type 2 diabetic patients and healthy subjects. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 88: 220–224, 2003 - PubMed
-
- Ahren B, Gomis R, Standl E, Mills D, Schweizer A: Twelve- and 52-week efficacy of the dipeptidyl peptidase IV inhibitor LAF237 in metformin-treated patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care 27: 2874–2880, 2004 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

