Deformity correction in children with hereditary hypophosphatemic rickets
- PMID: 18841431
- PMCID: PMC2628230
- DOI: 10.1007/s11999-008-0547-2
Deformity correction in children with hereditary hypophosphatemic rickets
Abstract
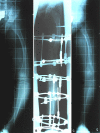
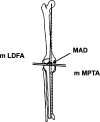
X-linked hereditary hypophosphatemic rickets can induce various multiplanar deformities of the lower limb. We evaluated our ability to correct these deformities and assessed complications and recurrence rates in 10 children (eight girls and a pair of twin boys) followed from early childhood to skeletal maturity. We performed 37 corrective operations in 10 children. Depending on the patient's age, external fixation was used in 53 segments: Kirschner wires in 18, DynaFix in three, the Taylor Spatial Frame device in 13, and the Ilizarov device in 19. Internal fixation with intramedullary nailing was performed in 12. After bone consolidation, we radiographically determined the mechanical axis at an average distance of 0.5 cm medial to the center of the knee. The average mechanical lateral distal femoral angle was 85 degrees (range, 83 degrees-92 degrees) and the average mechanical medial proximal tibial angle was 91 degrees (range, 85 degrees-92 degrees). Deviation of the mechanical axis and knee orientation lines was increased at the followups conducted during a period of 5 to 12 months. Additional followups revealed a recurrence rate of 90% after the first corrective procedure and 60% after a second procedure.
Level of evidence: Level IV, therapeutic study. See the Guidelines for Authors for a complete description of levels of evidence.
Figures



References
-
- None
- Albright F, Butler AM, Bloomberg E. Rickets resistant to vitamin D therapy. Am J Dis Child. 1937;54:529–547.
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'DOI', 'value': '10.1016/0002-9343(64)90085-3', 'is_inner': False, 'url': 'https://doi.org/10.1016/0002-9343(64)90085-3'}, {'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '14124689', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/14124689/'}]}
- Burnett CH, Dent CE, Harper C, Warland BJ. Vitamin D-resistant rickets: analysis of twenty-four pedigrees with hereditary and sporadic cases. Am J Med. 1964;36:222–232. - PubMed
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '6300745', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/6300745/'}]}
- Chesney RW, Mazess RB, Rose P, Hamstra AJ, DeLuca HF, Breed AL. Long-term influence of calcitriol (1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D) and supplemental phosphorous in X-linked hypophosphatemic rickets. Pediatrics. 1983;71:559–567. - PubMed
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'DOI', 'value': '10.1203/01.PDR.0000169983.40758.7B', 'is_inner': False, 'url': 'https://doi.org/10.1203/01.pdr.0000169983.40758.7b'}, {'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '16055933', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/16055933/'}]}
- Cho HY, Lee BH, Knag JH, Ha IS, Cheong HI, Choi Y. A clinical and molecular genetic study of hypophosphatemic rickets in children. Pediatr Res. 2005;58:329–333. - PubMed
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'DOI', 'value': '10.1097/00004694-200209000-00011', 'is_inner': False, 'url': 'https://doi.org/10.1097/00004694-200209000-00011'}, {'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '12198465', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/12198465/'}]}
- Choi IH, Kim JK, Chung CY, Cho TJ, Lee SH, Suh SW, Whang KS, Park HW, Song KS. Deformity correction of knee and leg lengthening by Ilizarov method in hypophosphatemic rickets: outcomes and significance of serum phosphate level. J Pediatr Orthop. 2002;22:626–631. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

