Telencephalon enlargement by the convergent evolution of expanded subventricular zones
- PMID: 18842571
- PMCID: PMC2657736
- DOI: 10.1098/rsbl.2008.0439
Telencephalon enlargement by the convergent evolution of expanded subventricular zones
Abstract
Some mammals and birds independently evolved an enlarged telencephalon. They appear to have done so, at least in part, by developing a thick telencephalic subventricular zone (SVZ). We suggest that this correlation between telencephalic enlargement and SVZ expansion is due to a mechanical constraint acting on the proliferative ventricular zone (VZ). Essentially, we argue that rapid proliferation in the VZ after post-mitotic cells in the overlying mantle zone have begun to form limits the VZ's tangential expandability and forces some proliferating cells to emigrate from the VZ and expand the pool of proliferating cells that comprise the SVZ.
Figures

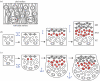
References
-
- Abdel-Mannan O., Cheung A.F., Molnár Z. Evolution of cortical neurogenesis. Brain Res. Bull. 2008;75:398–404. doi:10.1016/j.brainresbull.2007.10.047 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Boire D., Baron G. Allometric comparison of brain and main brain subdivisions in birds. J. Hirnforsch. 1994;35:49–66. - PubMed
-
- Charvet C.J., Striedter G.F. Developmental species differences in brain cell cycle rates between Northern bobwhite quail (Colinus virginianus) and parakeets (Melopsittacus undulatus): implications for mosaic brain evolution. Brain Behav. Evol. 2008;72:295–306. doi:10.1159/000184744 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Chenn A., Walsh C.A. Regulation of cerebral cortical size by control of cell cycle exit in neural precursors. Science. 2002;297:365–369. doi:10.1126/science.1074192 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
