A single in vivo application of cholinesterase inhibitors has neuron type-specific effects on nicotinic receptor activity in guinea pig hippocampus
- PMID: 18842705
- PMCID: PMC2685900
- DOI: 10.1124/jpet.108.146068
A single in vivo application of cholinesterase inhibitors has neuron type-specific effects on nicotinic receptor activity in guinea pig hippocampus
Abstract
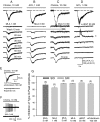
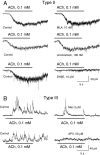
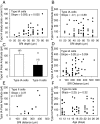
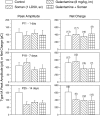
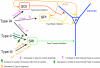
The present study was designed to test the hypothesis that an acute in vivo treatment with reversible or irreversible acetylcholinesterase (AChE) inhibitors modifies the activities of nicotinic receptors (nAChRs) in hippocampal neurons. Here, whole-cell nicotinic responses were recorded from CA1 interneurons in hippocampal slices obtained from male guinea pigs at 1, 7, or 14 days after treatment with the irreversible AChE inhibitor, soman (1x LD(50) s.c.), and/or the reversible AChE inhibitor, galantamine (8 mg/kg i.m.). Naive animals were used as controls. Three types of nAChR responses, namely types IA, II, and III, which were mediated by alpha 7, alpha 4 beta 2, and alpha 3 beta 2 beta 4 nAChRs, respectively, could be recorded from the interneurons. The magnitude of alpha 7 nAChR currents was neuron-type dependent. Stratum radiatum interneurons (SRIs) with thick initial dendrites had the largest alpha 7 nAChR currents. Acute challenge with soman caused sustained reduction of type IA current amplitudes recorded from stratum oriens interneurons and increased the ratio of acetylcholine- to choline-evoked current amplitudes recorded from SRIs. In guinea pigs that developed long-lasting convulsions after the soman challenge, there was a sustained reduction of alpha 3 beta 2 beta 4 nAChR responses. Acute treatment with galantamine had no effect on type IA or III responses, whereas it decreased the incidence of type II currents. Pretreatment of the guinea pigs with galantamine prevented the suppressive effect of soman on type III responses. The neuron type-specific changes in nAChR activity induced by soman, some of which could be prevented by galantamine, may contribute to the maintenance of pathological rhythms in the hippocampal neuronal network.
Figures







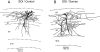
References
-
- Albuquerque EX, Deshpande SS, Kawabuchi M, Aracava Y, Idriss M, Rickett DL, and Boyne AF (1985) Multiple actions of anticholinesterase agents on chemosensitive synapses: molecular basis for prophylaxis and treatment of organophosphate poisoning. Fundam Appl Toxicol 5 S182-S203. - PubMed
-
- Alkondon M and Albuquerque EX (2001) Nicotinic acetylcholine receptor α7 and α4β2 subtypes differentially control GABAergic input to CA1 neurons in rat hippocampus. J Neurophysiol 86 3043-3055. - PubMed
-
- Alkondon M and Albuquerque EX (2004) The nicotinic acetylcholine receptor subtypes and their function in the hippocampus and cerebral cortex. Prog Brain Res 145 109-120. - PubMed
-
- Alkondon M and Albuquerque EX (2005) Nicotinic receptor subtypes in rat hippocampal slices are differentially sensitive to desensitization and early in vivo functional up-regulation by nicotine and to block by bupropion. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 313 740-750. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

