Acute coronary syndrome patients with depression have low blood cell membrane omega-3 fatty acid levels
- PMID: 18842751
- PMCID: PMC3579549
- DOI: 10.1097/PSY.0b013e318188a01e
Acute coronary syndrome patients with depression have low blood cell membrane omega-3 fatty acid levels
Abstract
Objective: To determine the extent to which levels of membrane eicosapentaenoic (EPA)+docosahexaenoic acids (DHA) (the omega-3 index) were associated with depression in patients with acute coronary syndrome (ACS). Depression is associated with worse cardiovascular (CV) outcomes in patients with ACS. Reduced levels of blood cell membrane omega-3 (n-3) fatty acids (FAs), an emerging risk factor for both CV disease and depression, may help to explain the link between depression and adverse CV outcomes.
Methods: We measured membrane FA composition in 759 patients with confirmed ACS. The analysis included not only EPA and DHA but also the n-6 FAs linoleic and arachidonic acids (LA and AA). Depressive symptoms were measured with the Patient Health Questionnaire-9 (PHQ). Multivariable linear regression was used to adjust for demographic and clinical characteristics.
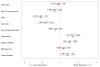
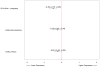
Results: There was a significant inverse relationship between the n-3 index and depressive symptoms (PHQ) in the fully adjusted model (p = .034). For every 4.54% point rise in the n-3 index, there was a 1-point decline in depressive symptoms. In contrast to the n-3 FAs, membrane levels of the n-6 FAs LA and AA were not different between depressed and nondepressed ACS patients.
Conclusion: We found an inverse relationship between the n-3 index and the prevalence of depressive symptoms in patients with ACS. Therefore, this study supports the hypothesis that reduced n-3 FA tissue levels are a common and potentially modifiable link between depression and adverse CV outcomes.
Figures
References
-
- Frasure-Smith N, Lesperance F, Talajic M. Depression and 18-month prognosis after myocardial infarction. Circulation. 1995;91:999– 1005. - PubMed
-
- Rozanski A, Blumenthal JA, Davidson KW, Saab PG, Kubzansky L. The epidemiology, pathophysiology, and management of psychosocial risk factors in cardiac practice: the emerging field of behavioral cardiology. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2005;45:637–51. - PubMed
-
- Kris-Etherton PM, Harris WS, Appel LJ. Fish consumption, fish oil, omega-3 fatty acids, and cardiovascular disease. Circulation. 2002;106:2747–57. - PubMed
-
- Meyer BJ, Mann NJ, Lewis JL, Milligan GC, Sinclair AJ, Howe PR. Dietary intakes and food sources of omega-6 and omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids. Lipids. 2003;38:391– 8. - PubMed
-
- Simopoulos AP, Leaf A, Salem N., Jr Essentiality of and recommended dietary intakes for omega-6 and omega-3 fatty acids. Ann Nutr Metab. 1999;43:127–30. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

