Embolization of intracranial arteriovenous malformations with ethylene-vinyl alcohol copolymer (Onyx)
- PMID: 18842759
- PMCID: PMC7051737
- DOI: 10.3174/ajnr.A1314
Embolization of intracranial arteriovenous malformations with ethylene-vinyl alcohol copolymer (Onyx)
Abstract
Background and purpose: Endovascular therapy of intracranial arteriovenous malformations (AVMs) is increasingly used. However, it is still under discussion which embolic material is optimal. We report our experience in the treatment of AVMs with ethylene-vinyl alcohol copolymer (Onyx).
Materials and methods: Between July 2002 and January 2008, brain AVMs were embolized with Onyx in 82 consecutive patients in our department. There were 41 females and 41 males with a mean age of 44.2 years (range, 15-85 years). Clinical presentation included symptoms due to intracerebral hemorrhage (n = 37), seizures (n = 18), nonhemorrhagic neurologic deficits (n = 8), headaches (n = 9), or incidental symptoms (n = 10). According to the Spetzler-Martin scale, 59 AVMs were grades I-II, 16 were grade III, and 7 were grades IV-V.
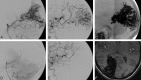
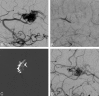
Results: Complete obliteration at the end of all endovascular procedures was achieved in 20/82 patients (24.4%), with an average of 75% (range, 30%-100%) volume reduction. A mean of 2.9 (range, 1-10) feeding pedicles was embolized per patient, whereas an average of 2.6-mL Onyx was used per patient. Procedure-related permanent disabling morbidity was 3.8%, whereas mortality was 2.4%.
Conclusions: The overall initial complete obliteration rate of intracranial AVMs with Onyx embolization is relatively high, compared with other embolic agents, with evidence of stability with time. Morbidomortality rates due to AVM embolization as a single treatment method or as a part of a multimodality treatment should be further assessed regarding the natural course of the disease.
Figures

Comment in
-
Embolization of brain arteriovenous malformations for cure: because we could or because we should?AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2009 Jan;30(1):107-8. doi: 10.3174/ajnr.A1394. Epub 2008 Nov 6. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2009. PMID: 18988684 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Berenstein A, Lasjaunias P, Ter Brugge KG. Goals and objectives in the management of brain arteriovenous malformations. In: Surgical Neuroangiography. 2nd ed. Berlin, Germany: Springer-Verlag Berlin;2004;695–735
-
- Luessenhop AJ, Presper JH. Surgical embolization of cerebral arteriovenous malformations through internal carotid and vertebral arteries: long-term results. J Neurosurg 1975;42:443–51 - PubMed
-
- Luessenhop AJ, Spence WJ. Artificial embolization of cerebral arteries: report of use in a case of arteriovenous malformations. JAMA 1960;172:1153–55 - PubMed
-
- Alexander MJ, Tolbert ME. Targeting cerebral arteriovenous malformations for minimally invasive therapy. Neurosurgery 2006;59 (5 suppl 3):S178–83, discussion S3–13 - PubMed
-
- Pasqualin A, Barone G, Cioffi F, et al. The relevance of anatomic and hemodynamic factors to a classification of cerebral arteriovenous malformations. Neurosurgery 1991;28:370–79 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
