Nutrigenetic association of the 5-lipoxygenase gene with myocardial infarction
- PMID: 18842779
- PMCID: PMC3014055
- DOI: 10.1093/ajcn/88.4.934
Nutrigenetic association of the 5-lipoxygenase gene with myocardial infarction
Abstract
Background: 5-Lipoxygenase (5-LO) catalyzes the rate-limiting step of the biosynthesis of proinflammatory leukotrienes from arachidonic acid (AA) and has been associated with atherosclerosis in animal models and humans. We previously reported that variants of a 5-LO promoter repeat polymorphism were associated with carotid atherosclerosis in humans, an effect that was exacerbated by high dietary AA but mitigated by high dietary n-3 fatty acids.
Objective: We sought to confirm these initial observations with a more clinically relevant phenotype such as myocardial infarction (MI).
Design: The 5-LO polymorphism was genotyped in 1885 Costa Rican case-control pairs and tested for association with MI. Functional experiments were carried out to determine whether the associated alleles had differences in mRNA expression.
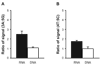
Results: The frequency of variant genotype groups did not differ significantly between cases and controls. However, a significant gene x diet interaction was observed, in which, relative to the common 5 repeat allele, the 3 and 4 alleles were associated with a higher MI risk in the high (> or = 0.25 g/d) dietary AA group (odds ratio: 1.31; 95% CI: 1.07, 1.61) and with a lower risk in the low (<0. 25 g/d) AA group (0.77; 0.63, 0.94) (P for interaction = 0.015). Using allele-specific quantitation, the short alleles had expression approximately twice that of the 5 allele (P < 0.0001).
Conclusions: The 3 and 4 variants lead to higher 5-LO expression and provide additional evidence that these alleles are associated with greater risks of atherosclerosis and MI in the context of a high-AA diet.
Figures

References
-
- Mehrabian M, Allayee H. 5-Lipoxygenase and atherosclerosis. Curr Opin Lipidol. 2003;14:447–457. - PubMed
-
- Tymchuk CN, Hartiala J, Patel PI, Mehrabian M, Allayee H. Nonconventional genetic risk factors for cardiovascular disease. Curr Atheroscler Rep. 2006;8:184–192. - PubMed
-
- Back M, Hansson GK. Leukotriene receptors in atherosclerosis. Ann Med. 2006;38:493–502. - PubMed
-
- Mehrabian M, Allayee H, Wong J, et al. Identification of 5-lipoxygenase as a major gene contributing to atherosclerosis susceptibility in mice. Circ Res. 2002;91:120–126. - PubMed
-
- Mehrabian M, Allayee H, Stockton J, et al. Integrating genotypic and expression data in a segregating mouse population to identify 5-lipoxygenase as a susceptibility gene for obesity and bone traits. Nat Genet. 2005;37:1224–1233. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

