Pioneer longitudinal axons navigate using floor plate and Slit/Robo signals
- PMID: 18842816
- PMCID: PMC2768610
- DOI: 10.1242/dev.023325
Pioneer longitudinal axons navigate using floor plate and Slit/Robo signals
Abstract
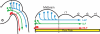
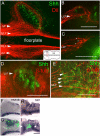
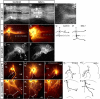
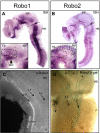
Longitudinal axons transmit all signals between the brain and spinal cord. Their axon tracts through the brain stem are established by a simple set of pioneer axons with precise trajectories parallel to the floor plate. To identify longitudinal guidance mechanisms in vivo, the overall role of floor plate tissue and the specific roles of Slit/Robo signals were tested. Ectopic induction or genetic deletion of the floor plate diverted longitudinal axons into abnormal trajectories. The expression patterns of the diffusible cues of the Slit family were altered in the floor plate experiments, suggesting their involvement in longitudinal guidance. Genetic tests of Slit1 and Slit2, and the Slit receptors Robo1 and Robo2 were carried out in mutant mice. Slit1;Slit2 double mutants had severe longitudinal errors, particularly for ventral axons, including midline crossing and wandering longitudinal trajectories. Robo1 and Robo2 were largely genetically redundant, and neither appeared to specify specific tract positions. However, combined Robo1 and Robo2 mutations strongly disrupted each pioneer tract. Thus, pioneer axons depend on long-range floor plate cues, with Slit/Robo signaling required for precise longitudinal trajectories.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Developmental guidance of the retroflex tract at its bending point involves Robo1-Slit2-mediated floor plate repulsion.Brain Struct Funct. 2016 Jan;221(1):665-78. doi: 10.1007/s00429-014-0932-4. Epub 2014 Nov 4. Brain Struct Funct. 2016. PMID: 25366972 Free PMC article.
-
Midbrain dopaminergic axons are guided longitudinally through the diencephalon by Slit/Robo signals.Mol Cell Neurosci. 2011 Jan;46(1):347-56. doi: 10.1016/j.mcn.2010.11.003. Epub 2010 Nov 27. Mol Cell Neurosci. 2011. PMID: 21118670 Free PMC article.
-
Collaborative and specialized functions of Robo1 and Robo2 in spinal commissural axon guidance.J Neurosci. 2010 Jul 14;30(28):9445-53. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.6290-09.2010. J Neurosci. 2010. PMID: 20631173 Free PMC article.
-
Robo1 and Robo2 have distinct roles in pioneer longitudinal axon guidance.Dev Biol. 2011 Oct 1;358(1):181-8. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2011.07.025. Epub 2011 Jul 23. Dev Biol. 2011. PMID: 21820427 Free PMC article.
-
Longitudinal axons are guided by Slit/Robo signals from the floor plate.Cell Adh Migr. 2010 Jul-Sep;4(3):337-41. doi: 10.4161/cam.4.3.11219. Epub 2010 Jul 18. Cell Adh Migr. 2010. PMID: 20215865 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Slit-Robo signals regulate pioneer axon pathfinding of the tract of the postoptic commissure in the mammalian forebrain.J Neurosci Res. 2011 Oct;89(10):1531-41. doi: 10.1002/jnr.22684. Epub 2011 Jun 17. J Neurosci Res. 2011. PMID: 21688288 Free PMC article.
-
A central role for Numb/Nbl in multiple Shh-mediated axon repulsion processes.iScience. 2025 Mar 26;28(5):112293. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2025.112293. eCollection 2025 May 16. iScience. 2025. PMID: 40276749 Free PMC article.
-
The expression pattern of EVA1C, a novel Slit receptor, is consistent with an axon guidance role in the mouse nervous system.PLoS One. 2013 Sep 9;8(9):e74115. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0074115. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 24040182 Free PMC article.
-
Developmental guidance of the retroflex tract at its bending point involves Robo1-Slit2-mediated floor plate repulsion.Brain Struct Funct. 2016 Jan;221(1):665-78. doi: 10.1007/s00429-014-0932-4. Epub 2014 Nov 4. Brain Struct Funct. 2016. PMID: 25366972 Free PMC article.
-
Slit-Robo signaling supports motor neuron avoidance of the spinal cord midline through DCC antagonism and other mechanisms.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2025 Apr 10;13:1563403. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2025.1563403. eCollection 2025. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2025. PMID: 40276653 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Agarwala S, Ragsdale CW. A role for midbrain arcs in nucleogenesis. Development. 2002;129:5779–5788. - PubMed
-
- Agarwala S, Sanders TA, Ragsdale CW. Sonic hedgehog control of size and shape in midbrain pattern formation. Science. 2001;291:2147–2150. - PubMed
-
- Andrews W, Liapi A, Plachez C, Camurri L, Zhang J, Mori S, Murakami F, Parnavelas JG, Sundaresan V, Richards LJ. Robo1 regulates the development of major axon tracts and interneuron migration in the forebrain. Development. 2006;133:2243–2252. - PubMed
-
- Bagri A, Marin O, Plump AS, Mak J, Pleasure SJ, Rubenstein JL, Tessier-Lavigne M. Slit proteins prevent midline crossing and determine the dorsoventral position of major axonal pathways in the mammalian forebrain. Neuron. 2002;33:233–248. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

