Inhibition of 2-oxoglutarate dehydrogenase in potato tuber suggests the enzyme is limiting for respiration and confirms its importance in nitrogen assimilation,
- PMID: 18842826
- PMCID: PMC2593666
- DOI: 10.1104/pp.108.126219
Inhibition of 2-oxoglutarate dehydrogenase in potato tuber suggests the enzyme is limiting for respiration and confirms its importance in nitrogen assimilation,
Abstract
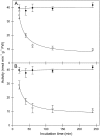
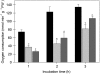
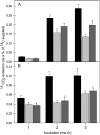
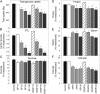
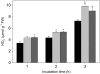
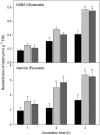
The 2-oxoglutarate dehydrogenase complex constitutes a mitochondrially localized tricarboxylic acid cycle multienzyme system responsible for the conversion of 2-oxoglutarate to succinyl-coenzyme A concomitant with NAD(+) reduction. Although regulatory mechanisms of plant enzyme complexes have been characterized in vitro, little is known concerning their role in plant metabolism in situ. This issue has recently been addressed at the cellular level in nonplant systems via the use of specific phosphonate inhibitors of the enzyme. Here, we describe the application of these inhibitors for the functional analysis of the potato (Solanum tuberosum) tuber 2-oxoglutarate dehydrogenase complex. In vitro experiments revealed that succinyl phosphonate (SP) and a carboxy ethyl ester of SP are slow-binding inhibitors of the 2-oxoglutarate dehydrogenase complex, displaying greater inhibitory effects than a diethyl ester of SP, a phosphono ethyl ester of SP, or a triethyl ester of SP. Incubation of potato tuber slices with the inhibitors revealed that they were adequately taken up by the tissue and produced the anticipated effects on the in situ enzyme activity. In order to assess the metabolic consequences of the 2-oxoglutarate dehydrogenase complex inhibition, we evaluated the levels of a broad range of primary metabolites using an established gas chromatography-mass spectrometry method. We additionally analyzed the rate of respiration in both tuber discs and isolated mitochondria. Finally, we evaluated the metabolic fate of radiolabeled acetate, 2-oxoglutarate or glucose, and (13)C-labeled pyruvate and glutamate following incubation of tuber discs in the presence or absence of either SP or the carboxy ethyl ester of SP. The data obtained are discussed in the context of the roles of the 2-oxoglutarate dehydrogenase complex in respiration and carbon-nitrogen interactions.
Figures



References
-
- Biryukov AI, Bunik VI, Zhukov YN, Khurs EN, Khomutov RM (1996) Succinyl phosphonate inhibits α-ketoglutarate oxidative decarboxylation, catalyzed by α-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase complexes from E. coli and pigeon breast muscle. FEBS Lett 382 167–170 - PubMed
-
- Bunik VI (2000) Increased catalytic performance of the 2-oxoacid dehydrogenase complexes in the presence of thioredoxin, a thiol-disulfide oxidoreductase. J Mol Catal B Enzym 8 165–174
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

