MicroRNA-9 modulates Cajal-Retzius cell differentiation by suppressing Foxg1 expression in mouse medial pallium
- PMID: 18842901
- PMCID: PMC6671033
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3219-08.2008
MicroRNA-9 modulates Cajal-Retzius cell differentiation by suppressing Foxg1 expression in mouse medial pallium
Abstract
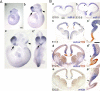
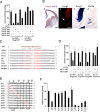
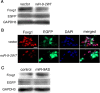
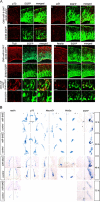
Vertebrate brain hosts a diverse collection of microRNAs, but little is known about their functions in vivo. Here we propose that mouse microRNA-9 (miR-9) targets Foxg1 mRNAs for proper generation of Cajal-Retzius cells in the medial pallium. miR-9 expression is mediolaterally graded, being most intense in the cortical hem; it contrasts with the Foxg1 expression in a reciprocal gradient. The 3' untranslated regions of tetrapod, but not of teleost, Foxg1 mRNAs conserve miR-9 target sequences and are regulated by miR-9. Gain- and loss-of-function analyses of miR-9 showed that miR-9 negatively regulates endogenous Foxg1 protein level. Moreover, miR-9 overexpression in developing telencephalon at E11.5 by electroporation resulted in ectopic Reelin-positive cells over the cortex beyond the marginal zone. In addition, inhibition of endogenous miR-9 function by antisense oligonucleotides caused the regression of Wnt3a-positive cortical hem and reduction of reelin-, p73-, and NeuroD1-positive cells.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Comparative aspects of p73 and Reelin expression in Cajal-Retzius cells and the cortical hem in lizard, mouse and human.Brain Res. 2007 Feb 9;1132(1):59-70. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2006.11.015. Epub 2006 Dec 26. Brain Res. 2007. PMID: 17189620
-
MicroRNA-9 regulates neurogenesis in mouse telencephalon by targeting multiple transcription factors.J Neurosci. 2011 Mar 2;31(9):3407-22. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5085-10.2011. J Neurosci. 2011. PMID: 21368052 Free PMC article.
-
Dynamic expression of the p53 family members p63 and p73 in the mouse and human telencephalon during development and in adulthood.Brain Res. 2011 Feb 4;1372:29-40. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2010.11.041. Epub 2010 Nov 27. Brain Res. 2011. PMID: 21114965
-
Building a human cortex: the evolutionary differentiation of Cajal-Retzius cells and the cortical hem.J Anat. 2010 Oct;217(4):334-43. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-7580.2010.01266.x. J Anat. 2010. PMID: 20626498 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Reelin, radial fibers and cortical evolution: insights from comparative analysis of the mammalian and avian telencephalon.Dev Growth Differ. 2009 Apr;51(3):287-97. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-169X.2008.01073.x. Epub 2008 Dec 19. Dev Growth Differ. 2009. PMID: 19210541 Review.
Cited by
-
MicroR-9-5p suppresses EV71 replication through targeting NFκB of the RIG-I-mediated innate immune response.FEBS Open Bio. 2018 Aug 29;8(9):1457-1470. doi: 10.1002/2211-5463.12490. eCollection 2018 Sep. FEBS Open Bio. 2018. Retraction in: FEBS Open Bio. 2023 Apr;13(4):795. doi: 10.1002/2211-5463.13583. PMID: 30186747 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
Exploring miR-9 Involvement in Ciona intestinalis Neural Development Using Peptide Nucleic Acids.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Mar 15;21(6):2001. doi: 10.3390/ijms21062001. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32183450 Free PMC article.
-
microRNA -378a-3p Restrains the Proliferation of Retinoblastoma Cells but Promotes Apoptosis of Retinoblastoma Cells via Inhibition of FOXG1.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2020 May 11;61(5):31. doi: 10.1167/iovs.61.5.31. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2020. PMID: 32428232 Free PMC article.
-
Prenatal exposure to valproic acid increases miR-132 levels in the mouse embryonic brain.Mol Autism. 2017 Jun 28;8:33. doi: 10.1186/s13229-017-0149-5. eCollection 2017. Mol Autism. 2017. PMID: 28670439 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNAs in Neural Stem Cells and Neurogenesis.Front Neurosci. 2012 Mar 12;6:30. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2012.00030. eCollection 2012. Front Neurosci. 2012. PMID: 22416227 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abramoff MD, Magelhaes PJ, Ram SJ. Image processing with ImageJ. Biophotonics Int. 2004;11:36–42.
-
- Bielle F, Griveau A, Narboux-Nême N, Vigneau S, Sigrist M, Arber S, Wassef M, Pierani A. Multiple origins of Cajal-Retzius cells at the borders of the developing pallium. Nat Neurosci. 2005;8:1002–1012. - PubMed
-
- Borrell V, Yoshimura Y, Callaway EM. Targeted gene delivery to telencephalic inhibitory neurons by directional in utero electroporation. J Neurosci Methods. 2005;143:151–158. - PubMed
-
- Bredenkamp N, Seoighe C, Illing N. Comparative evolutionary analysis of the FoxG1 transcription factor from diverse vertebrates identifies conserved recognition sites for microRNA regulation. Dev Genes Evol. 2007;217:227–233. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
