Control of core temperature and blood pressure stability during hemodialysis
- PMID: 18842948
- PMCID: PMC2615697
- DOI: 10.2215/CJN.01800408
Control of core temperature and blood pressure stability during hemodialysis
Abstract
Background and objectives: Cool dialysate may ameliorate intradialytic hypotension (IDH). It is not known whether it is sufficient to prevent an increase in core temperature (CT) during hemodialysis (HD) or whether a mild decline in CT would yield superior results. The aim of this study was to compare both approaches with regard to IDH.
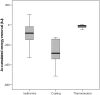
Design, setting, participants, & measurements: Fourteen HD patients with a history of IDH were studied. During three mid-week HD treatments, CT was set to decrease by 0.5 degrees C ("cooling") or to remain unchanged at the baseline level ("isothermic"). "Thermoneutral" HD (no energy is added to or removed from the patient) was used as a control. Central blood volume (CBV), BP, skin temperature, heart rate variability [low and high frequency] were recorded.
Results: CT increased during thermoneutral and remained respectively stable and decreased during isothermic and cooling. Skin temperature decreased significantly during isothermic and cooling, but not during thermoneutral. Nadir systolic BP (SBP) levels were lower during isothermic and thermoneutral compared with cooling. CBV tended to be higher during cooling compared with isothermic and thermoneutral. Three patients complained of shivering during cooling. Change in LF/HF was not different between cooling, isothermic, and thermoneutral.
Conclusions: IDH may be slightly improved by cooling compared with the isothermic approach, possibly because of improved maintenance of CBV. The hemodynamic effects of mild blood cooling should be balanced against a potentially higher risk of cold discomfort.
Figures

References
-
- Tisler A, Akocsi K, Borbas B, Fazakas L, Ferenczi S, Corogh S, Kulcsar I, Nagy L, Samik J, Szegedi J, Toth E, Wagner G, Kiss I: The effect of frequent or occasional dialysis-associated hypotension on survival of patients on maintenance haemodialysis. Nephrol Dial Transplant 18: 2601–2605, 2003 - PubMed
-
- Shoji T, Tsubakihara Y, Fujii M, Imai E: Hemodialysis-associated hypotension as an independent risk factor for two-year mortality in hemodialysis patients. Kidney Int 66: 1212–1220, 2004 - PubMed
-
- Kooman J, Basci A, Pizzarelli F, Canaud B, Haage P, Fouque D, Konner K, Martin-Malo A, Pedrini L, Tattersall J, Tordoir J, Vennegoor M, Wanner C, ter Wee P, Vanholder R: EBPG guideline on haemodynamic instability. Nephrol Dial Transplant 22[Suppl 2]: ii22–44, 2007 - PubMed
-
- Henderson LW: Hemodynamic instability during hemodialysis. Kidney Int 30: 605–612, 1986 - PubMed
-
- Schneditz D, Levin NW: Keep your temper: How to avoid heat accumulation in haemodialysis. Nephrol Dial Transplant 16: 7–9, 2001 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

