N-Terminal clustering of the O-glycosylation sites in the Mycobacterium tuberculosis lipoprotein SodC
- PMID: 18842962
- PMCID: PMC2733778
- DOI: 10.1093/glycob/cwn102
N-Terminal clustering of the O-glycosylation sites in the Mycobacterium tuberculosis lipoprotein SodC
Abstract
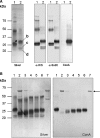
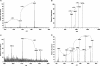
SodC is one of two superoxide dismutases produced by Mycobacterium tuberculosis. This protein was previously shown to contribute to virulence and to act as a B-cell antigen. SodC is also a putative lipoprotein, and like other Sec-translocated mycobacterial proteins it was suggested to be modified with glycosyl units. To definitively define the glycosylation of SodC, we applied an approach that combined site-directed mutagenesis, lectin binding, and mass spectrometry. This resulted in identification of six O-glycosylated residues within a 13-amino-acid region near the N-terminus. Each residue was modified with one to three hexose units, and the most dominant SodC glycoform was modified with nine hexose units. In addition to O-glycosylation of threonine residues, this study provides the first evidence of serine O-glycosylation in mycobacteria. When combined with bioinformatic analyses, the clustering of O-glycosylation appeared to occur in a region of SodC with a disordered structure and not in regions important to the enzymatic activity of SodC. The use of recombinant amino acid substitutions to alter glycosylation sites provided further evidence that glycosylation influences proteolytic processing and ultimately positioning of cell wall proteins.
Figures

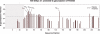




Similar articles
-
Bacterial glycoproteins: a link between glycosylation and proteolytic cleavage of a 19 kDa antigen from Mycobacterium tuberculosis.EMBO J. 1996 Jul 15;15(14):3547-54. EMBO J. 1996. PMID: 8670858 Free PMC article.
-
Evidence for glycosylation sites on the 45-kilodalton glycoprotein of Mycobacterium tuberculosis.Infect Immun. 1995 Aug;63(8):2846-53. doi: 10.1128/iai.63.8.2846-2853.1995. Infect Immun. 1995. PMID: 7622204 Free PMC article.
-
O-linked glycosylation sites profiling in Mycobacterium tuberculosis culture filtrate proteins.J Proteomics. 2014 Jan 31;97:296-306. doi: 10.1016/j.jprot.2013.05.011. Epub 2013 May 20. J Proteomics. 2014. PMID: 23702328 Free PMC article.
-
Identification and subcellular localization of a novel Cu,Zn superoxide dismutase of Mycobacterium tuberculosis.FEBS Lett. 1998 Nov 13;439(1-2):192-6. doi: 10.1016/s0014-5793(98)01373-8. FEBS Lett. 1998. PMID: 9849904
-
Mycobacteria and their sweet proteins: An overview of protein glycosylation and lipoglycosylation in M. tuberculosis.Tuberculosis (Edinb). 2019 Mar;115:1-13. doi: 10.1016/j.tube.2019.01.001. Epub 2019 Jan 14. Tuberculosis (Edinb). 2019. PMID: 30948163 Review.
Cited by
-
Bacterial protein-O-mannosylating enzyme is crucial for virulence of Mycobacterium tuberculosis.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013 Apr 16;110(16):6560-5. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1219704110. Epub 2013 Apr 2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013. PMID: 23550160 Free PMC article.
-
The cell envelope glycoconjugates of Mycobacterium tuberculosis.Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol. 2014 Sep-Oct;49(5):361-99. doi: 10.3109/10409238.2014.925420. Epub 2014 Jun 10. Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol. 2014. PMID: 24915502 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Evolution of Drug-Resistant Mycobacterium tuberculosis Strains and Their Adaptation to the Human Lung Environment.Front Microbiol. 2021 Feb 4;12:612675. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2021.612675. eCollection 2021. Front Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 33613483 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The sweet tooth of bacteria: common themes in bacterial glycoconjugates.Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2014 Sep;78(3):372-417. doi: 10.1128/MMBR.00007-14. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2014. PMID: 25184559 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Diversity in Mycobacterium tuberculosis mannosylated cell wall determinants impacts adaptation to the host.Tuberculosis (Edinb). 2010 Mar;90(2):84-93. doi: 10.1016/j.tube.2010.02.003. Epub 2010 Mar 3. Tuberculosis (Edinb). 2010. PMID: 20199890 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Abernathy JL, Wang Y, Eckhardt AE, Hill RL. Identification of O-glycosylation sites with a gas phase sequencer. In: Abernathy JL, editor. Techniques in Protein Chemistry. New York: Academic Press; 1992. pp. 277–286.
-
- Battistoni A, Rotilio G. Isolation of an active and heat-stable monomeric form of Cu, Zn superoxide dismutase from the periplasmic space of Escherichia coli. FEBS Lett. 1995;374:199–202. - PubMed
-
- Belisle JT, Braunstein M, Rosenkrands I, Andersen P. The proteome of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. In: Cole ST, editor. Tuberculosis and the Tubercle Bacillus. Washington, DC: ASM Press; 2005. pp. 235–260.
-
- Coligan JE. Current Protocols in Protein Science. 2001. p. 10.15.11. - PubMed

